Set up Kubernetes
Contents
Cheat sheet for setting up Kubernetes
If you need some help setting up a Kubernetes environment to experiment with the operator, please read on! The supported environments are either an on-premises installation of Kubernetes, for example, on bare metal, or on a cloud provider like Oracle Cloud, Microsoft Azure, Google, or Amazon. Cloud providers allow you to provision a managed Kubernetes environment from their management consoles. You could also set up Kubernetes manually using compute resources on a cloud. There are also a number of ways to run a Kubernetes single-node cluster that are suitable for development or testing purposes. Your options include:
“Production” options:
- Set up your own Kubernetes environment on bare compute resources on a cloud.
- Use your cloud provider’s management console to provision a managed Kubernetes environment.
- Install Kubernetes on your own compute resources (for example, “real” computers, outside a cloud).
“Development/test” options:
- Install Docker for Mac or Docker for Windows and enable its embedded Kubernetes cluster.
- We do not recommend or support other development/test options like Minikube, Minishift, kind, and so on.
We have provided our hints and tips for several of these options in the following sections.
Set up Kubernetes on bare compute resources in a cloud
Follow the basic steps from the Terraform OKE Module Installer for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
Prerequisites
- Download and install the Terraform OKE Module Installer for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
- Create directory for the Terraform module:
$ mkdir terraformmodule $ cd terraformmodule - Ensure that you have kubectl installed if you plan to interact with the cluster locally.
Quick start
The quick start uses the sample provided in Multi-region service mesh with Istio and OKE.
-
Do a
git cloneof the Terraform Kubernetes Installer project:$ git clone https://github.com/oracle-terraform-modules/terraform-oci-oke.git -
Run the following commands:
$ cd terraform-oci-oke/examples $ mkdir okewko $ cp -rf istio-mc okewko $ cd okewko -
Edit
c1.tfandc2.tfto add:allow_bastion_cluster_access = true bastion_is_public = true control_plane_is_public = true$ cp terraform.tfvars.example terraform.tfvars -
In the
terraform.tfvarsfile, update all values with the correct paths to the keys and IDs. -
Run the commands:
$ terraform init $ terraform plan $ terraform apply --auto-approveThis will create two OKE clusters.
-
Log in to the OCI dashboard.
a. Go to Developer Services > OKE clusters.
b. Select c1 cluster > Access Cluster.
c. Copy and paste this command to create the kubeconfig, for example:
$ oci ce cluster create-kubeconfig --cluster-id ocid1.cluster.oc1...... --file $HOME/.kube/config --region us-phoenix-1 --token-version 2.0.0 --kube-endpoint PUBLIC_ENDPOINT $ export KUBECONFIG= $HOME/.kube/config -
Verify that the cluster is accessible:
$ kubectl get nodes
Install Kubernetes on your own compute resources
For example, on Oracle Linux servers outside a cloud.
These instructions are for Oracle Linux 7u2+. If you are using a different flavor of Linux, you will need to adjust them accordingly.
These steps must be run with the root user, until specified otherwise! Any time you see YOUR_USERID in a command, you should replace it with your actual userid.
-
Choose the directories where your Docker and Kubernetes files will be stored. The Docker directory should be on a disk with a lot of free space (more than 100GB) because it will be used for the
/var/lib/dockerfile system, which contains all of your images and containers. The Kubernetes directory will be used for the/var/lib/kubeletfile system and persistent volume storage.$ export docker_dir=/scratch/docker$ export k8s_dir=/scratch/k8s_dir -
Create a shell script that sets up the necessary environment variables. You should probably just append this to the user’s
.bashrcso that it will get executed at login. You will also need to configure your proxy settings here if you are behind an HTTP proxy:#!/bin/bash export PATH=$PATH:/sbin:/usr/sbin pod_network_cidr="10.244.0.0/16" k8s_dir=$k8s_dir ## grab my IP address to pass into kubeadm init, and to add to no_proxy vars # assume ipv4 and eth0 ip_addr=`ip -f inet addr show eth0 | egrep inet | awk '{print $2}' | awk -F/ '{print $1}'\` export HTTPS_PROXY=http://proxy:80 export https_proxy=http://proxy:80 export NO_PROXY=localhost,127.0.0.1,.my.domain.com,/var/run/docker.sock,$pod_network_cidr,$ip_addr export no_proxy=localhost,127.0.0.1,.my.domain.com,/var/run/docker.sock,$pod_network_cidr,$ip_addr export HTTP_PROXY=http://proxy:80 export http_proxy=http://proxy:80 export KUBECONFIG=$k8s_dir/admin.confSource that script to set up your environment variables:
$ . ~/.bashrcIf you want command completion, you can add the following to the script:
[ -f /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion ] && . /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion source <(kubectl completion bash) -
Create the directories you need:
$ mkdir -p $docker_dir $k8s_dir/kubelet$ ln -s $k8s_dir/kubelet /var/lib/kubelet -
Set an environment variable with the Docker version you want to install:
$ docker_version="18.09.1.ol" -
Install Docker, removing any previously installed version:
### install docker and curl-devel (for git if needed)$ yum-config-manager --enable ol7_addons ol7_latest# we are going to just uninstall any docker-engine that is installed$ yum -y erase docker-engine docker-engine-selinux# now install the docker-engine at our specified version$ yum -y install docker-engine-$docker_version curl-devel -
Update the Docker options:
# edit /etc/sysconfig/docker to add custom OPTIONS$ cat /etc/sysconfig/docker | sed "s#^OPTIONS=.*#OPTIONS='--selinux-enabled --group=docker -g $docker_dir'#g" > /tmp/docker.out$ diff /etc/sysconfig/docker /tmp/docker.out$ mv /tmp/docker.out /etc/sysconfig/docker -
Set up the Docker network, including the HTTP proxy configuration, if you need it:
# generate a custom /setc/sysconfig/docker-network$ cat <<EOF > /etc/sysconfig/docker-network # /etc/sysconfig/docker-network DOCKER_NETWORK_OPTIONS="-H tcp://0.0.0.0:4243 -H unix:///var/run/docker.sock" HTTP_PROXY="http://proxy:80" HTTPS_PROXY="http://proxy:80" NO_PROXY="localhost,127.0.0.0/8,.my.domain.com,/var/run/docker.sock" EOF -
Add your user to the
dockergroup:$ usermod -aG docker YOUR_USERID -
Enable and start the Docker service that you just installed and configured:
$ systemctl enable docker && systemctl start docker -
Install the Kubernetes packages:
#!/bin/bash # generate the yum repo config cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo [kubernetes] name=Kubernetes baseurl=http://yum.kubernetes.io/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64 enabled=1 gpgcheck=1 repo_gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg EOF setenforce 0 # install kube* packages v=${1:-1.17.0-0} old_ver=`echo $v | egrep "^1.7"` yum install -y kubelet-$v kubeadm-$v kubectl-$v kubernetes-cni # change the cgroup-driver to match what docker is using cgroup=`docker info 2>&1 | egrep Cgroup | awk '{print $NF}'` [ "$cgroup" == "" ] && echo "cgroup not detected!" && exit 1 cat /etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service.d/10-kubeadm.conf | sed "s#KUBELET_CGROUP_ARGS=--cgroup-driver=.*#KUBELET_CGROUP_ARGS=--cgroup-driver=$cgroup\"#"> /etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service.d/10-kubeadm.conf.out diff /etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service.d/10-kubeadm.conf /etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service.d/10-kubeadm.conf.out mv /etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service.d/10-kubeadm.conf.out /etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service.d/10-kubeadm.conf if [ "$old_ver" = "" ] ; then # run with swap if not in version 1.7* (starting in 1.8, kubelet # fails to start with swap enabled) # cat <<EOF > /etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service.d/90-local-extras.conf [Service] Environment="KUBELET_EXTRA_ARGS=--fail-swap-on=false" EOF fi -
Enable and start the Kubernetes Service:
$ systemctl enable kubelet && systemctl start kubelet -
Install and use Flannel for CNI:
#!/bin/bash # run kubeadm init as root echo Running kubeadm init --skip-preflight-checks --apiserver-advertise-address=$ip_addr --pod-network-cidr=$pod_network_cidr echo " see /tmp/kubeadm-init.out for output" kubeadm init --skip-preflight-checks --apiserver-advertise-address=$ip_addr --pod-network-cidr=$pod_network_cidr > /tmp/kubeadm-init.out 2>&1 if [ $? -ne 0 ] ; then echo "ERROR: kubeadm init returned non 0" chmod a+r /tmp/kubeadm-init.out exit 1 else echo; echo "kubeadm init complete" ; echo # tail the log to get the "join" token tail -6 /tmp/kubeadm-init.out fi cp /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $KUBECONFIG chown YOUR_USERID:YOUR_GROUP $KUBECONFIG chmod 644 $KUBECONFIGThe following steps should be run with your normal (non-
root) user. -
Configure CNI:
$ sudo -u YOUR_USERID kubectl create clusterrolebinding permissive-binding --clusterrole=cluster-admin --user=admin --user=kubelet --group=system:serviceaccounts$ sudo -u YOUR_USERID kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.ymlWait for
kubectl get nodesto showReadyfor this host:#!/bin/bash host=`hostname | awk -F. '{print $1}'` status="NotReady" max=10 count=1 while [ ${status:=Error} != "Ready" -a $count -lt $max ] ; do sleep 30 status=`sudo -u YOUR_USERID kubectl get nodes | egrep $host | awk '{print $2}'` echo "kubectl status is ${status:=Error}, iteration $count of $max" count=`expr $count + 1` done status=`sudo -u YOUR_USERID kubectl get nodes | egrep $host | awk '{print $2}'` if [ ${status:=Error} != "Ready" ] ; then echo "ERROR: kubectl get nodes reports status=${status:=Error} after configuration, exiting!" exit 1 fi -
Taint the nodes:
$ sudo -u YOUR_USERID kubectl taint nodes --all node-role.kubernetes.io/master-$ sudo -u YOUR_USERID kubectl get nodes$ sudo -u YOUR_USERID kubeadm versionCongratulations! Docker and Kubernetes are installed and configured!
Install Docker for Mac with Kubernetes
Docker for Mac 18+ provides an embedded Kubernetes environment that is a quick and easy way to get a simple test environment set up on your Mac. To set it up, follow these instructions:
-
Install “Docker for Mac” https://download.docker.com/mac/edge/Docker.dmg. Then start up the Docker application (press Command-Space bar, type in
Dockerand run it). After it is running you will see the Docker icon appear in your status bar:
-
Click the Docker icon and select “Preferences…” from the drop down menu. Go to the “Advanced” tab and give Docker a bit more memory if you have enough to spare:
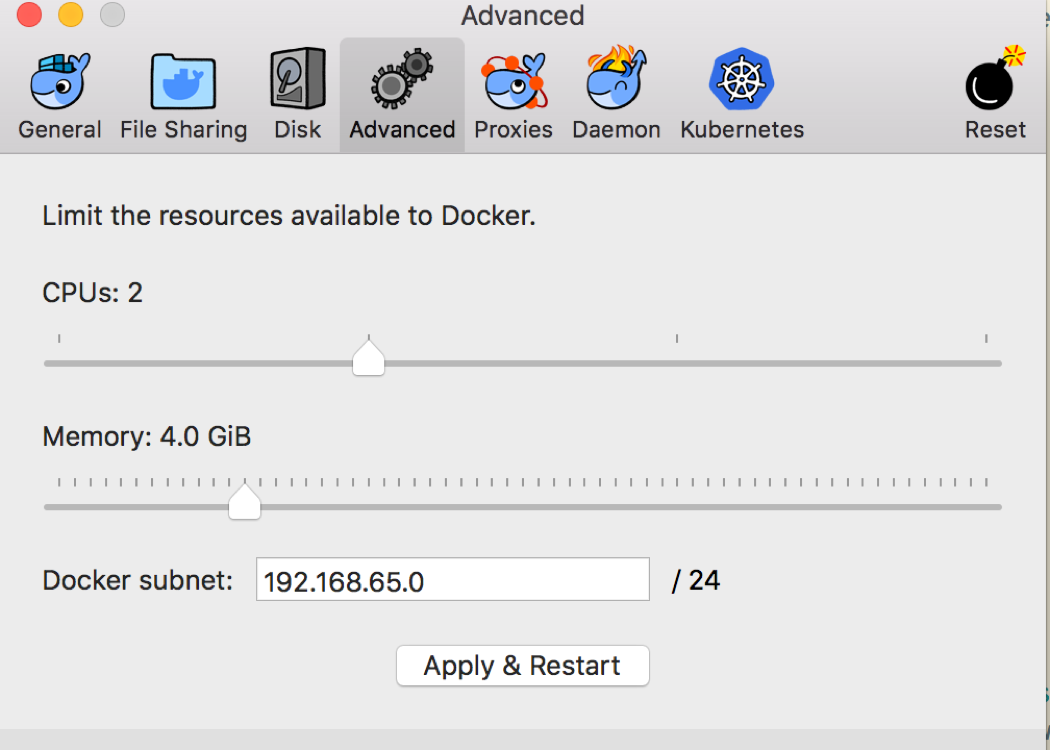
-
Go to the “Kubernetes” tab and click on the option to enable Kubernetes:
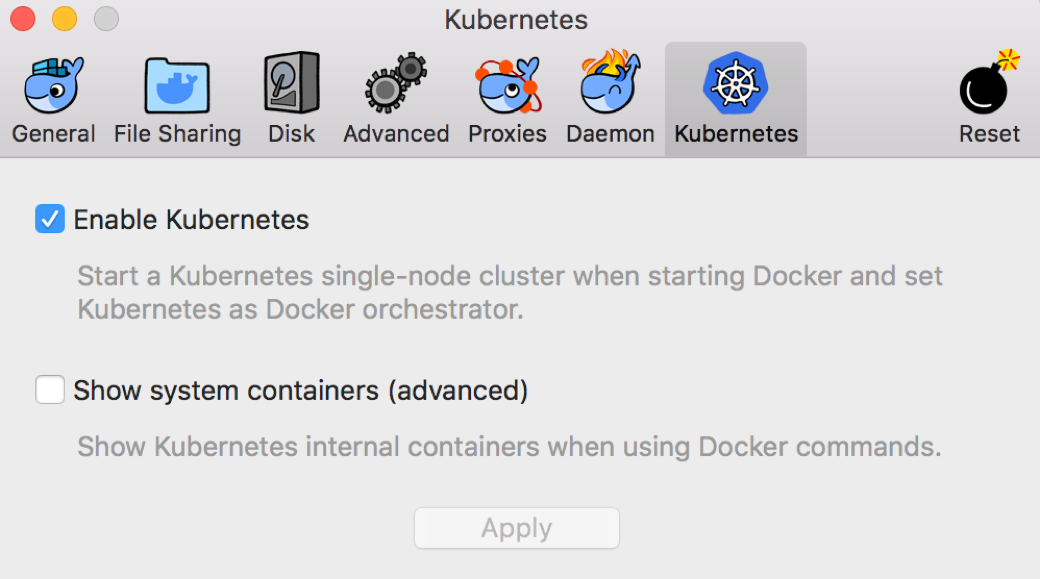
If you are behind an HTTP proxy, then you should also go to the “Proxies” tab and enter your proxy details.
Docker will download the Kubernetes components and start them up for you. When it is done, you will see the Kubernetes status go to green/running in the menu:
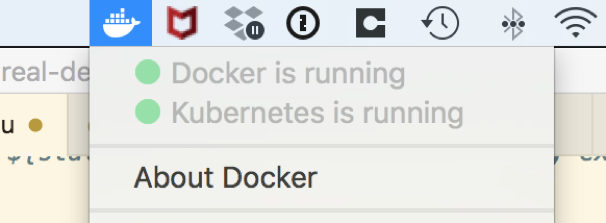
-
Ensure that
kubectlon your Mac, is pointing to the correct cluster and context.$ kubectl config get-contextsCURRENT NAME CLUSTER AUTHINFO NAMESPACE docker-for-desktop docker-for-desktop-cluster docker-for-desktop kubernetes-admin@kubernetes kubernetes kubernetes-admin$ kubectl config use-context docker-for-desktopSwitched to context "docker-for-desktop".$ kubectl config get-clustersNAME kubernetes docker-for-desktop-cluster$ kubectl config set-cluster docker-for-desktop-clusterCluster "docker-for-desktop-cluster" set. -
You should add
docker-for-desktopto your/etc/hostsfile entry for127.0.0.1, as shown in this example, and you must be an admin user to edit this file:## # Host Database # # localhost is used to configure the loopback interface # when the system is booting. Do not change this entry. ## 127.0.0.1 localhost docker-for-desktop 255.255.255.255 broadcasthost ::1 localhost -
You may also have to tell
kubectlto ignore the certificate by entering this command:$ kubectl config set-cluster docker-for-desktop --insecure-skip-tls-verify=true -
Then validate you are talking to the Kubernetes in Docker by entering these commands:
$ kubectl cluster-infoKubernetes master is running at https://docker-for-desktop:6443 To further debug and diagnose cluster problems, use 'kubectl cluster-info dump'.
Important note about persistent volumes
Docker for Mac has some restrictions on where you can place a directory that can be used as a HostPath for a persistent volume. To keep it simple, place your directory somewhere under /Users.