Database
The Oracle Backend for Spring Boot and Microservices uses the Oracle Database as a persistent data store for metadata and the Spring Cloud Config Server. This documentation will refer to this database as the Metadata Database.
NOTE: Oracle recommends that you install an addition Container Database (CDB) and Pluggable Databases (PDBs) for your production applications inline with the Database-Per-Service pattern. This document will refer to these databases as the Application Database.
By default, the Oracle Autonomous Database - Serverless (ADB-S) is used for the Metadata Database, however, there are other options including Bring Your Own (BYO).
The following chart presents the options for the Metadata Database, based on the installation type:
| Installation | ADB-S | BYO ADB-S | BYO BaseDB | BYO Containerized | BYO External |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OCI Community | x | ||||
| OCI Standard | x | x | x | x | |
| Custom | x | x | x | x | x |
For custom installations, including on-premises, it is the responsibility of the user to ensure network access controls to provide both operational access and security. The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Networking setup can be used as a general template.
If you select the Standard Edition during installation, you can use a pre-created Oracle Database for the Oracle Backend for Spring Boot and Microservices Metadata Database.
The following are the minimum requirements for a BYO Oracle Database:
- Version: 19c+
- Bring Your Own Network with access to the Database Listener
- Database User with appropriate privileges (see below)
The database user for the the Oracle Backend for Spring Boot and Microservices Metadata Database is used to create other users and allow them to proxy through this user for database access. While the SYSTEM or ADMIN (for ADB-S) will work, they are over-privileged and should not be used in production environments.
It is recommended to create a user, in this example, named OBAAS with a default tablespace of DATA:
CREATE USER OBAAS IDENTIFIED BY "Welcome_12345";
ALTER USER OBAAS QUOTA UNLIMITED ON DATA;
GRANT ALTER USER TO OBAAS;
GRANT CREATE USER TO OBAAS;
GRANT CONNECT TO OBAAS WITH ADMIN OPTION;
GRANT CREATE SESSION TO OBAAS WITH ADMIN OPTION;
GRANT RESOURCE TO OBAAS WITH ADMIN OPTION;
GRANT SELECT ON DBA_USERS TO OBAAS;
GRANT CREATE ANY INDEX TO OBAAS;
GRANT ALTER ANY TABLE TO OBAAS;
GRANT COMMENT ANY TABLE TO OBAAS;
GRANT CREATE ANY TABLE TO OBAAS;
GRANT INSERT ANY TABLE TO OBAAS;
GRANT SELECT ANY TABLE TO OBAAS;
GRANT UPDATE ANY TABLE TO OBAAS;
GRANT CREATE ANY SEQUENCE TO OBAAS;
GRANT SELECT ANY SEQUENCE TO OBAAS;
GRANT CREATE ANY TRIGGER TO OBAAS;
-- Additional AQ perms
GRANT AQ_USER_ROLE TO OBAAS WITH ADMIN OPTION;
GRANT EXECUTE ON DBMS_AQ TO OBAAS WITH GRANT OPTION;
GRANT EXECUTE ON DBMS_AQADM TO OBAAS WITH GRANT OPTION;
GRANT EXECUTE ON DBMS_AQIN TO OBAAS WITH GRANT OPTION;
GRANT EXECUTE ON DBMS_AQJMS TO OBAAS WITH GRANT OPTION;
GRANT EXECUTE ON DBMS_AQJMS_INTERNAL TO OBAAS WITH GRANT OPTION;
-- Additional for PARSE
GRANT SODA_APP TO OBAAS WITH ADMIN OPTION;
GRANT CREATE TABLE TO OBAAS WITH ADMIN OPTION;
-
During the configuration of the Oracle Backend for Spring Boot and Microservices, ensure that the Edition is set to Standard:
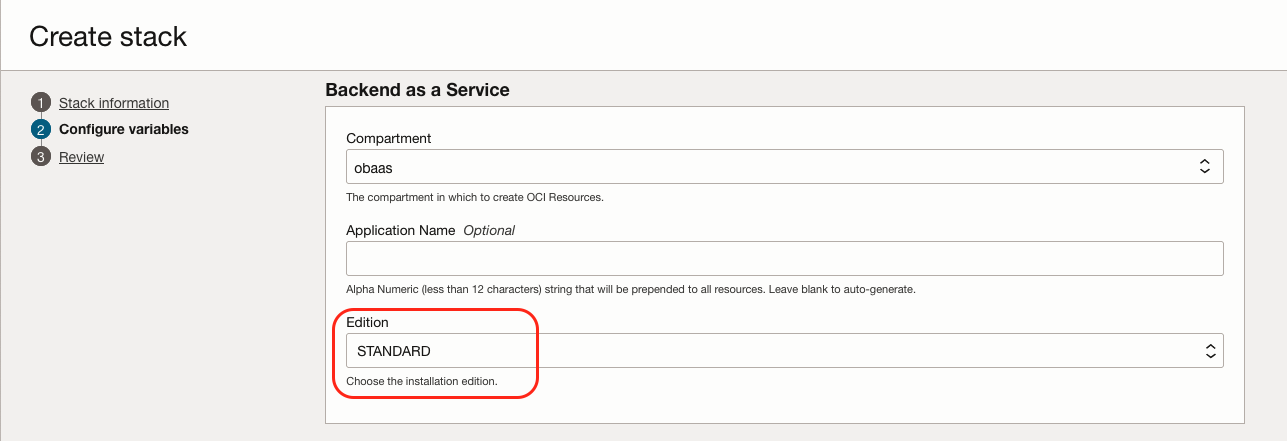
-
Enable and Configure Bring Your Own Virtual Network
-
Tick the “Bring Your Own Database” checkbox and, depending on the Bring Your Own Database - Type, provide the appropriate values.
-
BYO ADB-S Compartment: The compartment of the existing ADB-S. -
Bring Your Own Database - Autonomous Database: The ADB-S name (this will automatically translate the name to an OCID). -
Bring Your Own Database - Username: The existing database user with the appropriate privileges. -
Bring Your Own Database - Password: The password for the existing database user.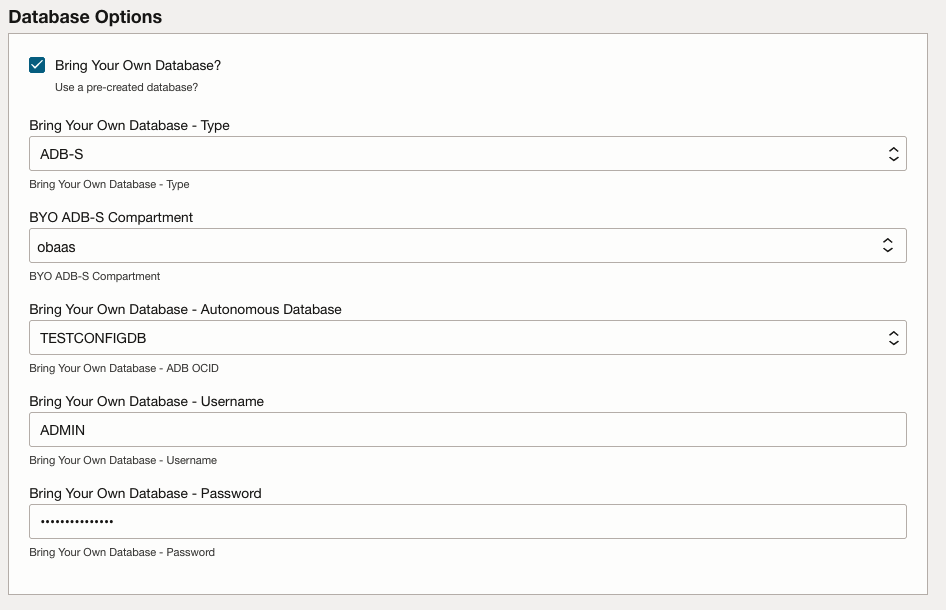
-
Bring Your Own Database - Connect String: The connect string for the database (PDB) in Long Format. -
Bring Your Own Database - Username: The existing database user with the appropriate privileges. -
Bring Your Own Database - Password: The password for the existing database user.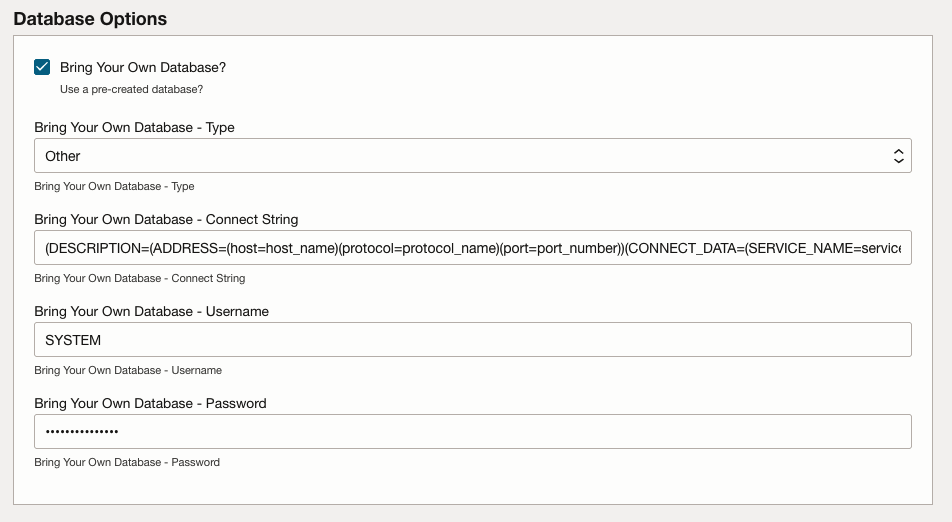
The Connect String should be in Long Format, for example:
(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(host=oracle://somedb.example.com)(protocol=TCP)(port=1521))
(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=orclpdb)))
Oracle recommends that additional pluggable databases are used for your applications, following the database-per-service microservice pattern. However, the Metadata Database can be used, especially for development purposes, with a schema-per-service model.
The Oracle Database Operator for Kubernetes is provided with the Oracle Backend for Spring Boot and Microservices and can be used:
- Bind to additional ADB-S
- Bind to an OCI BaseDB and create PDBs
- Create a Single Instance Container Database in the Kubernetes Cluster