Explore Spring Admin
Oracle Backend for Microservices and AI includes Spring Admin which provides a web user interface for managing and monitoring Spring applications.
-
Connect to Spring Admin
Oracle Backend for Microservices and AI does not expose management interfaces outside the Kubernetes cluster for improved security. Oracle recommends you access these interfaces using kubectl port forwarding, which creates an encrypted tunnel from your client machine to the cluster to access a specific service in the cluster.
Open a tunnel to the Spring Admin server using this command:
kubectl -n admin-server port-forward svc/admin-server 8989Open a web browser to http://localhost:8989 to view the Spring Admin web user interface.
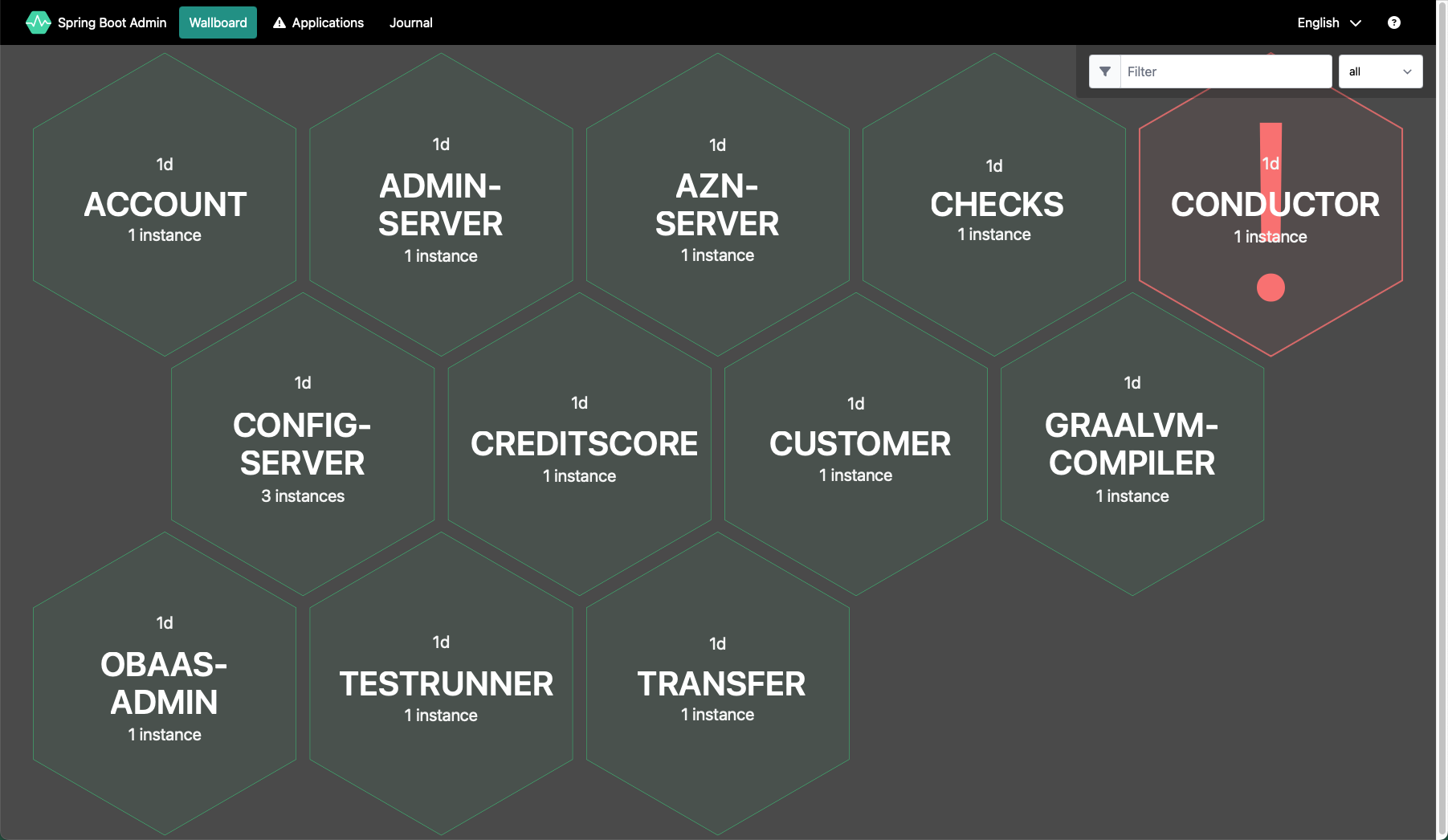
Click on the Wallboard link in the top menu to view the “wallboard” which shows all the discovered services. Spring Admin discovers services from the Spring Eureka Service Registry.
Each hexagon represents a service. Notice that this display gives you a quick overview of the health of your system. Green services are healthy, grey services have reduced availability and red services are not healthy. You can also see information about how many instances (i.e. pods) are available for each service.
-
View information about a service
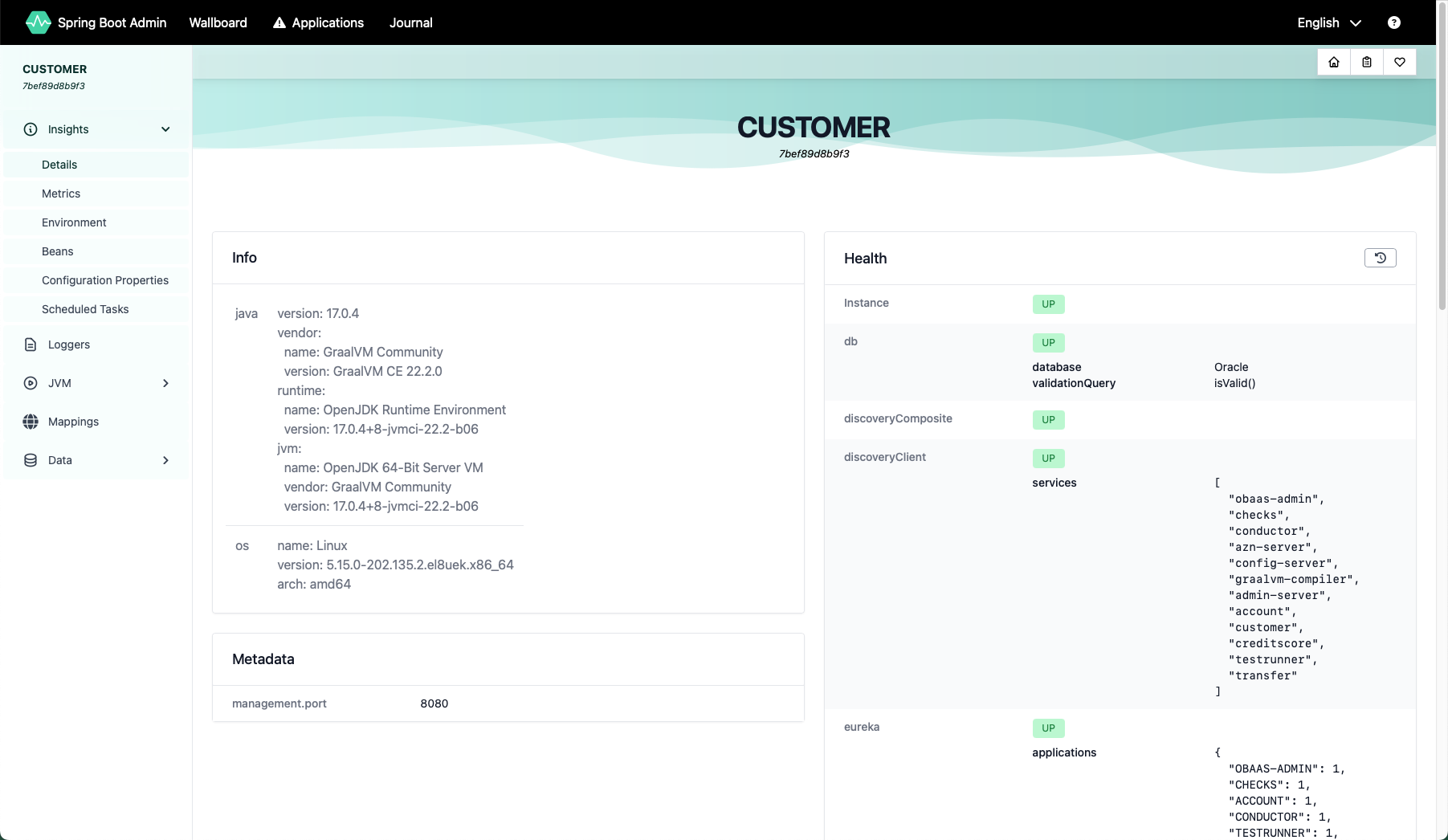
Click on the Customer service. You will see a detail page like this:
On this page, you can see detailed information about service’s health, and you can scroll down to see information about resource usage. The menu on the left hand side lets you view additional information about the service including its environment variables, the Spring beans loaded, its Spring configuration properties and so on. You can also access metrics from this interface.
-
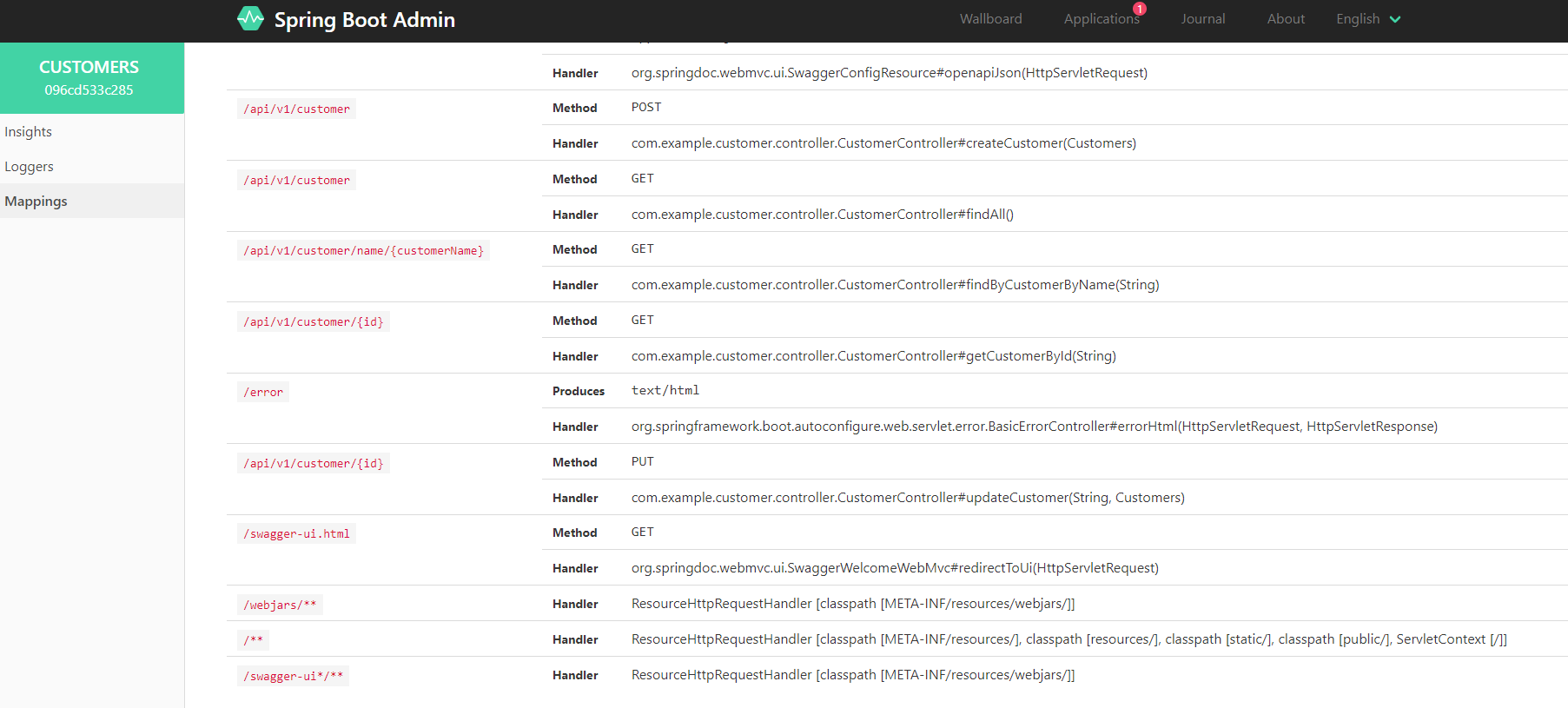
View endpoints
Click on the Mappings link on the left hand side menu. This page shows you information about the URL Path mappings (or endpoints) exposed by this service. You will notice several endpoints exposed by Spring Actuator, which enables this management and monitoring to be possible. And you will see your service’s own endpoints, in this example the ones that start with
/api/v1/...: