Create the Transfer service
Now, you will create another new Spring Boot microservice application and implement the Transfer Service. This service will initiate the LRA and act as the logical coordinator - it will call the deposit and withdraw services you just implemented to effect the transfer to process the Cloud Cash Payment.
-
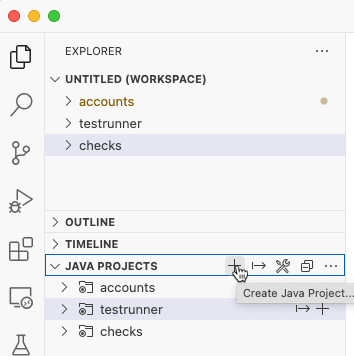
Create a new Java Project for the
transferservice.In the Explorer of VS Code open
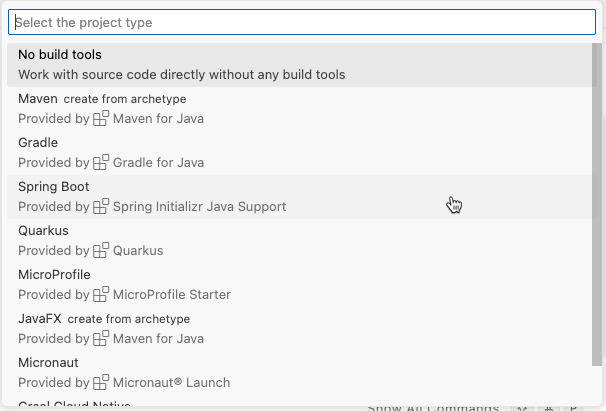
Java Projectand click the plus sign to add a Java Project to your workspace.Select Spring Boot Project.
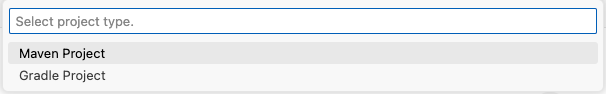
Select Maven Project.
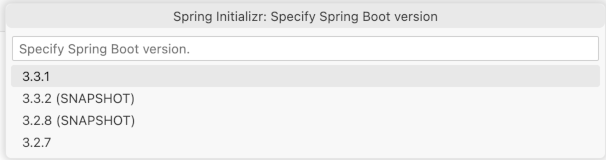
Specify
3.3.4as the Spring Boot version.Use
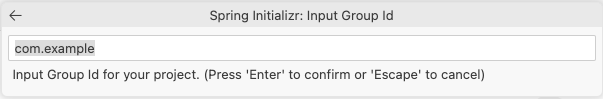
com.exampleas the Group Id.Enter
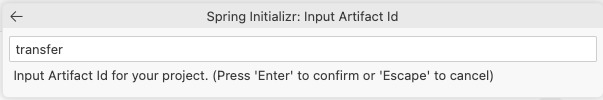
transferas the Artifact Id.Use
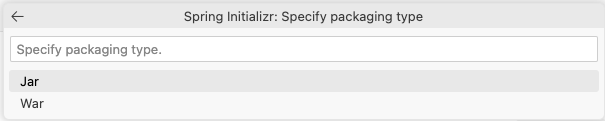
JARas the Packaging Type.Select Java version
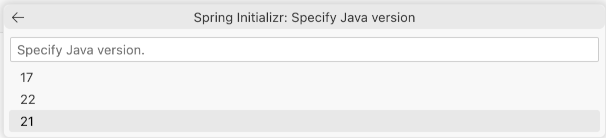
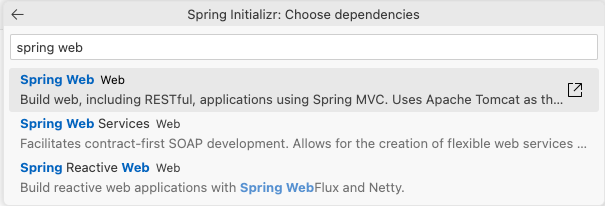
21.Search for
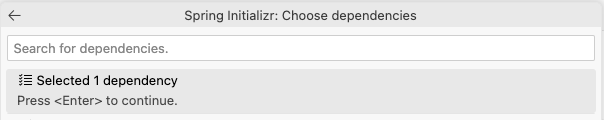
Spring Weband press EnterPress Enter to continue and create the Java Project
Select the
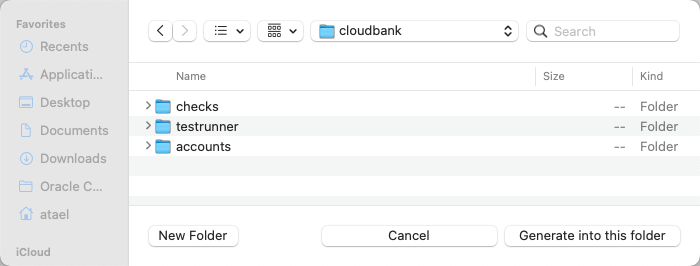
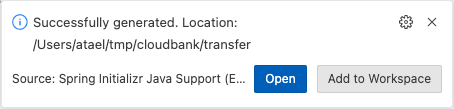
rootlocation for your project e.g. side by side with thechecks,testrunnerandaccountsprojects.When the project opens click Add to Workspace
-
Add MicroTX and Lombok to the
pom.xmlfileOpen the
pom.xmlfile in thetransferproject. Add the following to the pom.xml:<dependency> <groupId>com.oracle.microtx.lra</groupId> <artifactId>microtx-lra-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>23.4.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> </dependency> -
Create the Spring Boot application configuration
In the
transferproject, rename the file calledapplication.propertiestoapplication.yamllocated in thesrc/main/resources. This will be the Spring Boot application configuration file. In this file you need to configure the endpoints for the LRA participants and coordinator.spring: application: name: transfer mvc: enforced-prefixes: - /actuator - /rest url-mappings: - "/rest/*" - "/actuator/*" - "/error/*" microtx: lra: coordinator-url: ${MP_LRA_COORDINATOR_URL} propagation-active: true headers-propagation-prefix: "{x-b3-, oracle-tmm-, authorization, refresh-}" account: deposit: url: http://account.application:8080/deposit withdraw: url: http://account.application:8080/withdraw transfer: cancel: url: http://transfer.application:8080/cancel process: url: http://transfer.application:8080/processcancel confirm: url: http://transfer.application:8080/confirm process: url: http://transfer.application:8080/processconfirm -
Create the Transfer service
You are now ready to implement the main logic for the Cloud Cash Payment/transfer LRA. You will implement this in a new Java file called
TransferService.javainsrc/main/java/com/example/transfer. Here are the imports you will need for this class and the member variables. Note that this class has the@RestControllerand@RequestMappingannotations, as you saw previously in the Account project, to set up the URL context root for the service.package com.example.transfer; import java.net.URI; import com.oracle.microtx.springboot.lra.annotation.Compensate; import com.oracle.microtx.springboot.lra.annotation.Complete; import com.oracle.microtx.springboot.lra.annotation.LRA; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.http.HttpEntity; import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders; import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestHeader; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate; import org.springframework.web.util.UriComponentsBuilder; import static com.oracle.microtx.springboot.lra.annotation.LRA.LRA_HTTP_CONTEXT_HEADER; @RestController @RequestMapping("/") @Slf4j public class TransferService { public static final String TRANSFER_ID = "TRANSFER_ID"; @Value("${account.withdraw.url}") URI withdrawUri; @Value("${account.deposit.url}") URI depositUri; @Value("${transfer.cancel.url}") URI transferCancelUri; @Value("${transfer.cancel.process.url}") URI transferProcessCancelUri; @Value("${transfer.confirm.url}") URI transferConfirmUri; @Value("${transfer.confirm.process.url}") URI transferProcessConfirmUri; } -
Create the transfer endpoint
This is the main entry point for the LRA. When a client calls this method, a new LRA will be started. The
@LRAannotation with thevalueproperty set toLRA.Type.REQUIRES_NEWinstructs the interceptors/filters to contact Oracle Transaction Manager for Microservices to start a new LRA instance and obtain the LRA ID, which will be injected into theLRA_HTTP_CONTEXT_HEADERHTTP header. Note that theendproperty is set tofalsewhich means there will be other actions and participants before the LRA is completed.This method will accept three parameters from the caller, in JSON format in the HTTP body:
fromAccountis the account from which the funds are to be withdrawn,toAccountis the account into which the funds are to be deposited, andamountis the amount to transfer.In the method body, you should first check if the
lraIdwas set. If it is null, that indicates that there was some error trying to create the new LRA instance, and you should return an error response and stop.After that, you want to perform the withdrawal, check if it worked, and if so, perform the deposit, and then check if that worked, and if so “complete” the LRA. If there were any failures, compensate the LRA.
/** * Transfer amount between two accounts. * @param fromAccount From an account * @param toAccount To an account * @param amount Amount to transfer * @param lraId LRA Id * @return TO-DO */ @PostMapping("/transfer") @LRA(value = LRA.Type.REQUIRES_NEW, end = false) public ResponseEntity<String> transfer(@RequestParam("fromAccount") long fromAccount, @RequestParam("toAccount") long toAccount, @RequestParam("amount") long amount, @RequestHeader(LRA_HTTP_CONTEXT_HEADER) String lraId) { if (lraId == null) { return new ResponseEntity<>("Failed to create LRA", HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR); } log.info("Started new LRA/transfer Id: " + lraId); boolean isCompensate = false; String returnString = ""; // perform the withdrawal returnString += withdraw(lraId, fromAccount, amount); log.info(returnString); if (returnString.contains("succeeded")) { // if it worked, perform the deposit returnString += " " + deposit(lraId, toAccount, amount); log.info(returnString); if (returnString.contains("failed")) { isCompensate = true; // deposit failed } } else { isCompensate = true; // withdraw failed } log.info("LRA/transfer action will be " + (isCompensate ? "cancel" : "confirm")); // call complete or cancel based on outcome of previous actions RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(); HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders(); headers.setContentType(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN); headers.set(TRANSFER_ID, lraId); HttpEntity<String> request = new HttpEntity<String>("", headers); ResponseEntity<String> response = restTemplate.postForEntity( (isCompensate ? transferCancelUri : transferConfirmUri).toString(), request, String.class); returnString += response.getBody(); // return status return ResponseEntity.ok("transfer status:" + returnString); } -
Create a method to perform the withdrawal
This method should perform the withdrawal by calling the Withdraw service in the Account Spring Boot application. The
lraId,accountIdandamountneed to be passed to the service, and you must set theLRA_HTTP_CONTEXT_HEADERto the LRA ID.private String withdraw(String lraId, long accountId, long amount) { log.info("withdraw accountId = " + accountId + ", amount = " + amount); log.info("withdraw lraId = " + lraId); UriComponentsBuilder builder = UriComponentsBuilder.fromUri(withdrawUri) .queryParam("accountId", accountId) .queryParam("amount", amount); RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(); HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders(); headers.setContentType(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN); headers.set(LRA_HTTP_CONTEXT_HEADER, lraId.toString()); HttpEntity<String> request = new HttpEntity<String>("", headers); ResponseEntity<String> response = restTemplate.postForEntity( builder.buildAndExpand().toUri(), request, String.class); return response.getBody(); } -
Create a method to perform the deposit
This method is similar the previous one, no new concepts are introduced here.
private String deposit(String lraId, long accountId, long amount) { log.info("deposit accountId = " + accountId + ", amount = " + amount); log.info("deposit lraId = " + lraId); UriComponentsBuilder builder = UriComponentsBuilder.fromUri(depositUri) .queryParam("accountId", accountId) .queryParam("amount", amount); RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(); HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders(); headers.setContentType(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN); headers.set(LRA_HTTP_CONTEXT_HEADER, lraId.toString()); HttpEntity<String> request = new HttpEntity<String>("", headers); ResponseEntity<String> response = restTemplate.postForEntity( builder.buildAndExpand().toUri(), request, String.class); return response.getBody(); } -
Create a method to process the confirm action for this participant
This participant does not need to take any actions for the confirm action, so just return a successful response.
@PostMapping("/processconfirm") @LRA(value = LRA.Type.MANDATORY) public ResponseEntity<String> processconfirm(@RequestHeader(LRA_HTTP_CONTEXT_HEADER) String lraId) { log.info("Process confirm for transfer : " + lraId); return ResponseEntity.ok(""); } -
Create a method to process the cancel action for this participant
This participant does not need to take any actions for the cancel action, so just return a successful response.
@PostMapping("/processcancel") @LRA(value = LRA.Type.MANDATORY, cancelOn = HttpStatus.OK) public ResponseEntity<String> processcancel(@RequestHeader(LRA_HTTP_CONTEXT_HEADER) String lraId) { log.info("Process cancel for transfer : " + lraId); return ResponseEntity.ok(""); } -
Create the confirm and cancel methods
The logic demonstrated in these two methods would probably be in a client in a real-life LRA, but is included here for instructional purposes and convenience.
The
transfermethod makes a REST call to confirm (or cancel) at the end of its processing. The confirm or cancel method suspends the LRA (using theNOT_SUPPORTEDvaluein the@LRAannotation). Then the confirm or cancel method will make a REST call toprocessconfirmorprocesscancelwhich import the LRA with theirMANDATORYannotation and then implicitly end the LRA accordingly upon returning./** * Confirm a transfer. * @param transferId Transfer Id * @return TO-DO */ @PostMapping("/confirm") @Complete @LRA(value = LRA.Type.NOT_SUPPORTED) public ResponseEntity<String> confirm(@RequestHeader(TRANSFER_ID) String transferId) { log.info("Received confirm for transfer : " + transferId); RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(); HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders(); headers.setContentType(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN); headers.set(LRA_HTTP_CONTEXT_HEADER, transferId); HttpEntity<String> request = new HttpEntity<String>("", headers); ResponseEntity<String> response = restTemplate.postForEntity( transferProcessConfirmUri, request, String.class); return ResponseEntity.ok(response.getBody()); } /** * Cancel a transfer. * @param transferId Transfer Id * @return TO-DO */ @PostMapping("/cancel") @Compensate @LRA(value = LRA.Type.NOT_SUPPORTED, cancelOn = HttpStatus.OK) public ResponseEntity<String> cancel(@RequestHeader(TRANSFER_ID) String transferId) { log.info("Received cancel for transfer : " + transferId); RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(); HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders(); headers.setContentType(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN); headers.set(LRA_HTTP_CONTEXT_HEADER, transferId); HttpEntity<String> request = new HttpEntity<String>("", headers); ResponseEntity<String> response = restTemplate.postForEntity( transferProcessCancelUri, request, String.class); return ResponseEntity.ok(response.getBody()); }That completes the Transfer service and application.