VectorIndex supports Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG).
For e.g., you can convert text into vector embeddings and store them in a
vector store. Select AI will augment the natural language prompt by retrieving
content from the vector store using semantic similarity search.
1. VectorIndex Object Model¶
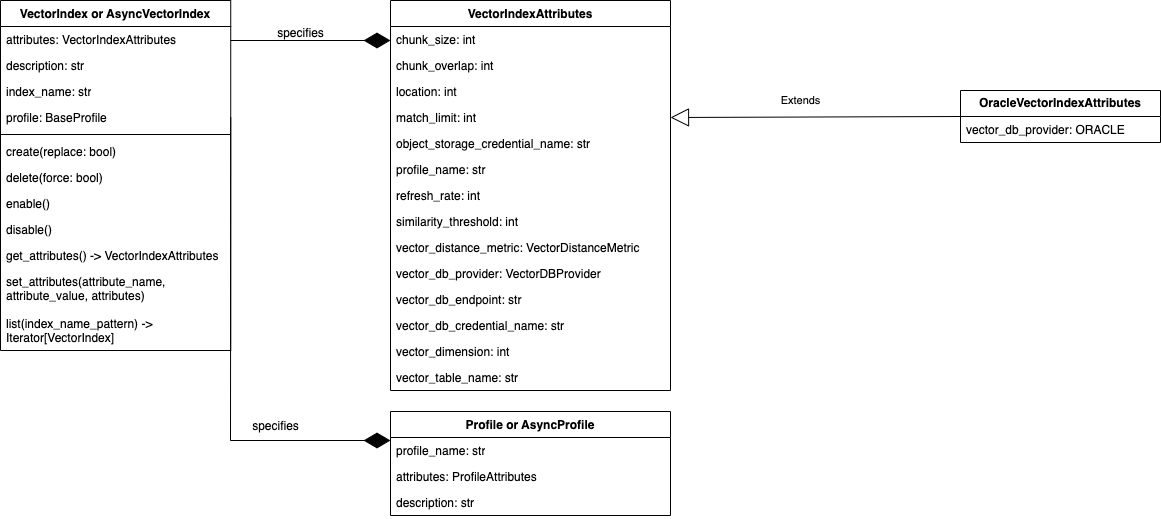
2. VectorIndexAttributes¶
A VectorIndexAttributes object can be created with
select_ai.VectorIndexAttributes(). Also check
vector index attributes
- class select_ai.VectorIndexAttributes(chunk_size: int | None = None, chunk_overlap: int | None = None, location: str | None = None, match_limit: int | None = None, object_storage_credential_name: str | None = None, profile_name: str | None = None, refresh_rate: int | None = None, similarity_threshold: float | None = None, vector_distance_metric: VectorDistanceMetric | None = None, vector_db_endpoint: str | None = None, vector_db_credential_name: str | None = None, vector_db_provider: VectorDBProvider | None = None, vector_dimension: int | None = None, vector_table_name: str | None = None, pipeline_name: str | None = None)¶
Attributes of a vector index help to manage and configure the behavior of the vector index.
- Parameters:
chunk_size (int) – Text size of chunking the input data.
chunk_overlap (int) – Specifies the amount of overlapping characters between adjacent chunks of text.
location (str) – Location of the object store.
match_limit (int) – Specifies the maximum number of results to return in a vector search query
object_storage_credential_name (str) – Name of the credentials for accessing object storage.
profile_name (str) – Name of the AI profile which is used for embedding source data and user prompts.
refresh_rate (int) – Interval of updating data in the vector store. The unit is minutes.
similarity_threshold (float) – Defines the minimum level of similarity required for two items to be considered a match
vector_distance_metric (VectorDistanceMetric) – Specifies the type of distance calculation used to compare vectors in a database
vector_db_provider (VectorDBProvider) – Name of the Vector database provider. Default value is “oracle”
vector_db_endpoint (str) – Endpoint to access the Vector database
vector_db_credential_name (str) – Name of the credentials for accessing Vector database
vector_dimension (int) – Specifies the number of elements in each vector within the vector store
vector_table_name (str) – Specifies the name of the table or collection to store vector embeddings and chunked data
2.1. OracleVectorIndexAttributes¶
- class select_ai.OracleVectorIndexAttributes(chunk_size: int | None = None, chunk_overlap: int | None = None, location: str | None = None, match_limit: int | None = None, object_storage_credential_name: str | None = None, profile_name: str | None = None, refresh_rate: int | None = None, similarity_threshold: float | None = None, vector_distance_metric: VectorDistanceMetric | None = None, vector_db_endpoint: str | None = None, vector_db_credential_name: str | None = None, vector_db_provider: VectorDBProvider | None = VectorDBProvider.ORACLE, vector_dimension: int | None = None, vector_table_name: str | None = None, pipeline_name: str | None = None)¶
Oracle specific vector index attributes
3. VectorIndex API¶
A VectorIndex object can be created with select_ai.VectorIndex()
- class select_ai.VectorIndex(profile: BaseProfile | None = None, index_name: str | None = None, description: str | None = None, attributes: VectorIndexAttributes | None = None)¶
VectorIndex objects let you manage vector indexes
- Parameters:
index_name (str) – The name of the vector index
description (str) – The description of the vector index
attributes (select_ai.VectorIndexAttributes) – The attributes of the vector index
- create(replace: bool | None = False)¶
- Create a vector index in the database and populates the index
with data from an object store bucket using an async scheduler job
- Parameters:
replace (bool) – Replace vector index if it exists
- Returns:
None
- delete(include_data: bool | None = True, force: bool | None = False)¶
This procedure removes a vector store index
- Parameters:
include_data (bool) – Indicates whether to delete both the customer’s vector store and vector index along with the vector index object
force (bool) – Indicates whether to ignore errors that occur if the vector index does not exist
- Returns:
None
- Raises:
oracledb.DatabaseError
- classmethod delete_index(index_name: str, include_data: bool = True, force: bool = False)¶
Class method to remove a vector store index
- Parameters:
index_name (str) – The name of the vector index
include_data (bool) – Indicates whether to delete both the customer’s vector store and vector index along with the vector index object
force (bool) – Indicates whether to ignore errors that occur if the vector index does not exist
- Returns:
None
- Raises:
oracledb.DatabaseError
- disable()¶
This procedure disables a vector index object in the current database. When disabled, an AI profile cannot use the vector index, and the system does not load data into the vector store as new data is added to the object store and does not perform indexing, searching or querying based on the index.
- Returns:
None
- Raises:
oracledb.DatabaseError
- enable()¶
This procedure enables or activates a previously disabled vector index object. Generally, when you create a vector index, by default it is enabled such that the AI profile can use it to perform indexing and searching.
- Returns:
None
- Raises:
oracledb.DatabaseError
- classmethod fetch(index_name: str) VectorIndex¶
Fetches vector index attributes from the database and builds a proxy object for the passed index_name
- Parameters:
index_name (str) – The name of the vector index
- get_attributes() VectorIndexAttributes¶
Get attributes of this vector index
- Returns:
select_ai.VectorIndexAttributes
- Raises:
VectorIndexNotFoundError
- get_profile() Profile¶
Get Profile object linked to this vector index
- Returns:
select_ai.Profile
- Raises:
ProfileNotFoundError
- classmethod list(index_name_pattern: str = '.*') Iterator[VectorIndex]¶
List Vector Indexes
- Parameters:
index_name_pattern (str) – Regular expressions can be used to specify a pattern. Function REGEXP_LIKE is used to perform the match. Default value is “.*” i.e. match all vector indexes.
- Returns:
Iterator[VectorIndex]
- set_attribute(attribute_name: str, attribute_value: str | int | float)¶
This procedure updates an existing vector store index with a specified value of the vector index attribute.
- Parameters:
attribute_name (str) – Custom attribute name
attribute_value (Union[str, int, float]) – Attribute Value
- set_attributes(attributes: VectorIndexAttributes = None)¶
This procedure updates an existing vector store index with a specified value of the vector index attributes. Specify multiple attributes by passing an object of type :class VectorIndexAttributes
- Parameters:
attributes (select_ai.VectorIndexAttributes) – Use this to update multiple attribute values
- Returns:
None
- Raises:
oracledb.DatabaseError
Check the examples below to understand how to create vector indexes
3.1. Create vector index¶
In the following example, vector database provider is Oracle and objects (to create embedding for) reside in OCI’s object store
import os
import select_ai
user = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_USER")
password = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_PASSWORD")
dsn = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_DB_CONNECT_STRING")
select_ai.connect(user=user, password=password, dsn=dsn)
# Configure an AI provider with an embedding model
# of your choice
provider = select_ai.OCIGenAIProvider(
region="us-chicago-1",
oci_apiformat="GENERIC",
embedding_model="cohere.embed-english-v3.0",
)
# Create an AI profile to use the Vector index with
profile_attributes = select_ai.ProfileAttributes(
credential_name="my_oci_ai_profile_key",
provider=provider,
)
profile = select_ai.Profile(
profile_name="oci_vector_ai_profile",
attributes=profile_attributes,
description="MY OCI AI Profile",
replace=True,
)
# Specify objects to create an embedding for. In this example,
# the objects reside in ObjectStore and the vector database is
# Oracle
vector_index_attributes = select_ai.OracleVectorIndexAttributes(
location="https://objectstorage.us-ashburn-1.oraclecloud.com/n/dwcsdev/b/conda-environment/o/tenant1-pdb3/graph",
object_storage_credential_name="my_oci_ai_profile_key",
)
# Create a Vector index object
vector_index = select_ai.VectorIndex(
index_name="test_vector_index",
attributes=vector_index_attributes,
description="Test vector index",
profile=profile,
)
vector_index.create(replace=True)
print("Created vector index: test_vector_index")
output:
Created vector index: test_vector_index
3.2. List vector index¶
import os
import select_ai
user = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_USER")
password = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_PASSWORD")
dsn = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_DB_CONNECT_STRING")
select_ai.connect(user=user, password=password, dsn=dsn)
vector_index = select_ai.VectorIndex()
for index in vector_index.list(index_name_pattern="^test"):
print("Vector index", index.index_name)
print("Vector index profile", index.profile)
output:
Vector index TEST_VECTOR_INDEX
Vector index profile Profile(profile_name=oci_vector_ai_profile, attributes=ProfileAttributes(annotations=None, case_sensitive_values=None, comments=None, constraints=None, conversation=None, credential_name='my_oci_ai_profile_key', enable_sources=None, enable_source_offsets=None, enforce_object_list=None, max_tokens=1024, object_list=None, object_list_mode=None, provider=OCIGenAIProvider(embedding_model=None, model=None, provider_name='oci', provider_endpoint=None, region='us-chicago-1', oci_apiformat='GENERIC', oci_compartment_id=None, oci_endpoint_id=None, oci_runtimetype=None), seed=None, stop_tokens=None, streaming=None, temperature=None, vector_index_name='test_vector_index'), description=None)
3.3. Fetch vector index¶
You can fetch the vector index attributes and associated AI profile using
the class method VectorIndex.fetch(index_name)
import os
import select_ai
user = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_USER")
password = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_PASSWORD")
dsn = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_DB_CONNECT_STRING")
select_ai.connect(user=user, password=password, dsn=dsn)
vector_index = select_ai.VectorIndex.fetch(index_name="test_vector_index")
print(vector_index.attributes)
print(vector_index.profile)
output:
OracleVectorIndexAttributes(chunk_size=1024, chunk_overlap=128, location='https://objectstorage.us-ashburn-1.oraclecloud.com/n/dwcsdev/b/conda-environment/o/tenant1-pdb3/graph', match_limit=5, object_storage_credential_name='my_oci_ai_profile_key', profile_name='oci_vector_ai_profile', refresh_rate=1450, similarity_threshold=0.5, vector_distance_metric='COSINE', vector_db_endpoint=None, vector_db_credential_name=None, vector_db_provider=<VectorDBProvider.ORACLE: 'oracle'>, vector_dimension=None, vector_table_name=None, pipeline_name='TEST_VECTOR_INDEX$VECPIPELINE')
Profile(profile_name=oci_vector_ai_profile, attributes=ProfileAttributes(annotations=None, case_sensitive_values=None, comments=None, constraints=None, conversation=None, credential_name='my_oci_ai_profile_key', enable_custom_source_uri=None, enable_sources=None, enable_source_offsets=None, enforce_object_list=None, max_tokens=1024, object_list=None, object_list_mode=None, provider=OCIGenAIProvider(embedding_model='cohere.embed-english-v3.0', model=None, provider_name='oci', provider_endpoint=None, region='us-chicago-1', oci_apiformat='GENERIC', oci_compartment_id=None, oci_endpoint_id=None, oci_runtimetype=None), seed=None, stop_tokens=None, streaming=None, temperature=None, vector_index_name='test_vector_index'), description=MY OCI AI Profile)
3.4. Update vector index attributes¶
To update attributes, use either vector_index.set_attribute() or
vector_index.set_attributes()
import os
import select_ai
user = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_USER")
password = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_PASSWORD")
dsn = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_DB_CONNECT_STRING")
select_ai.connect(user=user, password=password, dsn=dsn)
vector_index = select_ai.VectorIndex(
index_name="test_vector_index",
)
# Use vector_index.set_attributes to update a multiple attributes
updated_attributes = select_ai.OracleVectorIndexAttributes(refresh_rate=1450)
vector_index.set_attributes(attributes=updated_attributes)
# Use vector_index.set_attribute to update a single attribute
vector_index.set_attribute(
attribute_name="similarity_threshold", attribute_value=0.5
)
print(vector_index.attributes)
output:
OracleVectorIndexAttributes(chunk_size=1024, chunk_overlap=128, location='https://objectstorage.us-ashburn-1.oraclecloud.com/n/dwcsdev/b/conda-environment/o/tenant1-pdb3/graph', match_limit=5, object_storage_credential_name='my_oci_ai_profile_key', profile_name='oci_vector_ai_profile', refresh_rate=1450, similarity_threshold=0.5, vector_distance_metric='COSINE', vector_db_endpoint=None, vector_db_credential_name=None, vector_db_provider=<VectorDBProvider.ORACLE: 'oracle'>, vector_dimension=None, vector_table_name=None, pipeline_name='TEST_VECTOR_INDEX$VECPIPELINE')
3.5. RAG using vector index¶
import os
import select_ai
user = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_USER")
password = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_PASSWORD")
dsn = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_DB_CONNECT_STRING")
select_ai.connect(user=user, password=password, dsn=dsn)
profile = select_ai.Profile(profile_name="oci_vector_ai_profile")
r = profile.narrate("list the conda environments in my object store")
print(r)
output:
The conda environments in your object store are:
1. fccenv
2. myrenv
3. fully-loaded-mlenv
4. graphenv
These environments are listed in the provided data as separate JSON documents, each containing information about a specific conda environment.
Sources:
- fccenv-manifest.json (https://objectstorage.us-ashburn-1.oraclecloud.com/n/dwcsdev/b/conda-environment/o/tenant1-pdb3/graph/fccenv-manifest.json)
- myrenv-manifest.json (https://objectstorage.us-ashburn-1.oraclecloud.com/n/dwcsdev/b/conda-environment/o/tenant1-pdb3/graph/myrenv-manifest.json)
- fully-loaded-mlenv-manifest.json (https://objectstorage.us-ashburn-1.oraclecloud.com/n/dwcsdev/b/conda-environment/o/tenant1-pdb3/graph/fully-loaded-mlenv-manifest.json)
- graphenv-manifest.json (https://objectstorage.us-ashburn-1.oraclecloud.com/n/dwcsdev/b/conda-environment/o/tenant1-pdb3/graph/graphenv-manifest.json)
3.6. Delete vector index¶
import os
import select_ai
user = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_USER")
password = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_PASSWORD")
dsn = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_DB_CONNECT_STRING")
select_ai.connect(user=user, password=password, dsn=dsn)
vector_index = select_ai.VectorIndex(index_name="test_vector_index")
vector_index.delete(force=True)
print("Deleted vector index: test_vector_index")
output:
Deleted vector index: test_vector_index
4. AsyncVectorIndex API¶
A AsyncVectorIndex object can be created with select_ai.AsyncVectorIndex()
- class select_ai.AsyncVectorIndex(profile: BaseProfile | None = None, index_name: str | None = None, description: str | None = None, attributes: VectorIndexAttributes | None = None)¶
AsyncVectorIndex objects let you manage vector indexes using async APIs. Use this for non-blocking concurrent requests
- Parameters:
index_name (str) – The name of the vector index
description (str) – The description of the vector index
attributes (VectorIndexAttributes) – The attributes of the vector index
- async create(replace: bool | None = False) None¶
Create a vector index in the database and populates it with data from an object store bucket using an async scheduler job
- Parameters:
replace (bool) – True to replace existing vector index
- async delete(include_data: bool | None = True, force: bool | None = False) None¶
This procedure removes a vector store index.
- Parameters:
include_data (bool) – Indicates whether to delete both the customer’s vector store and vector index along with the vector index object.
force (bool) – Indicates whether to ignore errors that occur if the vector index does not exist.
- Returns:
None
- Raises:
oracledb.DatabaseError
- async classmethod delete_index(index_name: str, include_data: bool = True, force: bool = False)¶
Class method to remove a vector store index
- Parameters:
index_name (str) – The name of the vector index
include_data (bool) – Indicates whether to delete both the customer’s vector store and vector index along with the vector index object
force (bool) – Indicates whether to ignore errors that occur if the vector index does not exist
- Returns:
None
- Raises:
oracledb.DatabaseError
- async disable() None¶
This procedure disables a vector index object in the current database. When disabled, an AI profile cannot use the vector index, and the system does not load data into the vector store as new data is added to the object store and does not perform indexing, searching or querying based on the index.
- Returns:
None
- Raises:
oracledb.DatabaseError
- async enable() None¶
This procedure enables or activates a previously disabled vector index object. Generally, when you create a vector index, by default it is enabled such that the AI profile can use it to perform indexing and searching.
- Returns:
None
- Raises:
oracledb.DatabaseError
- async classmethod fetch(index_name: str) AsyncVectorIndex¶
Fetches vector index attributes from the database and builds a proxy object for the passed index_name
- Parameters:
index_name (str) – The name of the vector index
- async get_attributes() VectorIndexAttributes¶
Get attributes of a vector index
- Returns:
select_ai.VectorIndexAttributes
- Raises:
VectorIndexNotFoundError
- async get_profile() AsyncProfile¶
Get AsyncProfile object linked to this vector index
- Returns:
select_ai.AsyncProfile
- Raises:
ProfileNotFoundError
- classmethod list(index_name_pattern: str = '.*') AsyncGenerator[AsyncVectorIndex, None]¶
List Vector Indexes.
- Parameters:
index_name_pattern (str) – Regular expressions can be used to specify a pattern. Function REGEXP_LIKE is used to perform the match. Default value is “.*” i.e. match all vector indexes.
- Returns:
AsyncGenerator[VectorIndex]
- async set_attribute(attribute_name: str, attribute_value: str | int | float) None¶
This procedure updates an existing vector store index with a specified value of the vector index attribute.
- Parameters:
attribute_name (str) – Custom attribute name
attribute_value (Union[str, int, float]) – Attribute Value
- async set_attributes(attributes: VectorIndexAttributes) None¶
This procedure updates an existing vector store index with a specified value of the vector index attribute. multiple attributes by passing an object of type :class VectorIndexAttributes
- Parameters:
attributes (select_ai.VectorIndexAttributes) – Use this to update multiple attribute values
- Returns:
None
- Raises:
oracledb.DatabaseError
4.1. Async create vector index¶
import asyncio
import os
import select_ai
user = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_USER")
password = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_PASSWORD")
dsn = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_DB_CONNECT_STRING")
async def main():
await select_ai.async_connect(user=user, password=password, dsn=dsn)
provider = select_ai.OCIGenAIProvider(
region="us-chicago-1",
oci_apiformat="GENERIC",
embedding_model="cohere.embed-english-v3.0",
)
profile_attributes = select_ai.ProfileAttributes(
credential_name="my_oci_ai_profile_key",
provider=provider,
)
async_profile = await select_ai.AsyncProfile(
profile_name="async_oci_vector_ai_profile",
attributes=profile_attributes,
description="MY OCI AI Profile",
replace=True,
)
vector_index_attributes = select_ai.OracleVectorIndexAttributes(
location="https://objectstorage.us-ashburn-1.oraclecloud.com/n/dwcsdev/b/conda-environment/o/tenant1-pdb3/graph",
object_storage_credential_name="my_oci_ai_profile_key",
)
async_vector_index = select_ai.AsyncVectorIndex(
index_name="test_vector_index",
attributes=vector_index_attributes,
description="Vector index for conda environments",
profile=async_profile,
)
await async_vector_index.create(replace=True)
print("Created vector index: test_vector_index")
asyncio.run(main())
output:
created vector index: test_vector_index
4.2. Async list vector index¶
import asyncio
import os
import select_ai
user = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_USER")
password = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_PASSWORD")
dsn = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_DB_CONNECT_STRING")
async def main():
await select_ai.async_connect(user=user, password=password, dsn=dsn)
vector_index = select_ai.AsyncVectorIndex()
async for index in vector_index.list(index_name_pattern="^test"):
print("Vector index", index.index_name)
print("Vector index profile", index.profile)
asyncio.run(main())
output:
Vector index TEST_VECTOR_INDEX
Vector index profile AsyncProfile(profile_name=oci_vector_ai_profile, attributes=ProfileAttributes(annotations=None, case_sensitive_values=None, comments=None, constraints=None, conversation=None, credential_name='my_oci_ai_profile_key', enable_sources=None, enable_source_offsets=None, enforce_object_list=None, max_tokens=1024, object_list=None, object_list_mode=None, provider=OCIGenAIProvider(embedding_model=None, model=None, provider_name='oci', provider_endpoint=None, region='us-chicago-1', oci_apiformat='GENERIC', oci_compartment_id=None, oci_endpoint_id=None, oci_runtimetype=None), seed=None, stop_tokens=None, streaming=None, temperature=None, vector_index_name='test_vector_index'), description=None)
4.3. Async fetch vector index¶
You can fetch the vector index attributes and associated AI profile using
the class method AsyncVectorIndex.fetch(index_name)
import asyncio
import os
import select_ai
user = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_USER")
password = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_PASSWORD")
dsn = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_DB_CONNECT_STRING")
async def main():
await select_ai.async_connect(user=user, password=password, dsn=dsn)
async_vector_index = await select_ai.AsyncVectorIndex.fetch(
index_name="test_vector_index"
)
print(async_vector_index.attributes)
print(async_vector_index.profile)
asyncio.run(main())
output:
OracleVectorIndexAttributes(chunk_size=1024, chunk_overlap=128, location='https://objectstorage.us-ashburn-1.oraclecloud.com/n/dwcsdev/b/conda-environment/o/tenant1-pdb3/graph', match_limit=5, object_storage_credential_name='my_oci_ai_profile_key', profile_name='oci_vector_ai_profile', refresh_rate=1450, similarity_threshold=0.5, vector_distance_metric='COSINE', vector_db_endpoint=None, vector_db_credential_name=None, vector_db_provider=<VectorDBProvider.ORACLE: 'oracle'>, vector_dimension=None, vector_table_name=None, pipeline_name='TEST_VECTOR_INDEX$VECPIPELINE')
AsyncProfile(profile_name=oci_vector_ai_profile, attributes=ProfileAttributes(annotations=None, case_sensitive_values=None, comments=None, constraints=None, conversation=None, credential_name='my_oci_ai_profile_key', enable_custom_source_uri=None, enable_sources=None, enable_source_offsets=None, enforce_object_list=None, max_tokens=1024, object_list=None, object_list_mode=None, provider=OCIGenAIProvider(embedding_model='cohere.embed-english-v3.0', model=None, provider_name='oci', provider_endpoint=None, region='us-chicago-1', oci_apiformat='GENERIC', oci_compartment_id=None, oci_endpoint_id=None, oci_runtimetype=None), seed=None, stop_tokens=None, streaming=None, temperature=None, vector_index_name='test_vector_index'), description=MY OCI AI Profile)
4.4. Async update vector index attributes¶
To update attributes, use either async_vector_index.set_attribute() or
async_vector_index.set_attributes()
import asyncio
import os
import select_ai
user = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_USER")
password = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_PASSWORD")
dsn = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_DB_CONNECT_STRING")
async def main():
await select_ai.async_connect(user=user, password=password, dsn=dsn)
async_vector_index = select_ai.AsyncVectorIndex(
index_name="test_vector_index",
)
# Use vector_index.set_attributes to update a multiple attributes
updated_attributes = select_ai.OracleVectorIndexAttributes(
refresh_rate=1450
)
await async_vector_index.set_attributes(attributes=updated_attributes)
# Use vector_index.set_attribute to update a single attribute
await async_vector_index.set_attribute(
attribute_name="similarity_threshold", attribute_value=0.5
)
print(async_vector_index.attributes)
asyncio.run(main())
output:
OracleVectorIndexAttributes(chunk_size=1024, chunk_overlap=128, location='https://objectstorage.us-ashburn-1.oraclecloud.com/n/dwcsdev/b/conda-environment/o/tenant1-pdb3/graph', match_limit=5, object_storage_credential_name='my_oci_ai_profile_key', profile_name='oci_vector_ai_profile', refresh_rate=1450, similarity_threshold=0.5, vector_distance_metric='COSINE', vector_db_endpoint=None, vector_db_credential_name=None, vector_db_provider=<VectorDBProvider.ORACLE: 'oracle'>, vector_dimension=None, vector_table_name=None, pipeline_name='TEST_VECTOR_INDEX$VECPIPELINE')
4.5. Async RAG using vector index¶
import os
import select_ai
user = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_USER")
password = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_PASSWORD")
dsn = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_DB_CONNECT_STRING")
async def main():
await select_ai.async_connect(user=user, password=password, dsn=dsn)
async_profile = await select_ai.AsyncProfile(
profile_name="async_oci_vector_ai_profile"
)
r = await async_profile.narrate(
"list the conda environments in my object store"
)
print(r)
asyncio.run(main())
output:
The conda environments in your object store are:
1. fccenv
2. myrenv
3. fully-loaded-mlenv
4. graphenv
These environments are listed in the provided data as separate JSON documents, each containing information about a specific conda environment.
Sources:
- fccenv-manifest.json (https://objectstorage.us-ashburn-1.oraclecloud.com/n/dwcsdev/b/conda-environment/o/tenant1-pdb3/graph/fccenv-manifest.json)
- myrenv-manifest.json (https://objectstorage.us-ashburn-1.oraclecloud.com/n/dwcsdev/b/conda-environment/o/tenant1-pdb3/graph/myrenv-manifest.json)
- fully-loaded-mlenv-manifest.json (https://objectstorage.us-ashburn-1.oraclecloud.com/n/dwcsdev/b/conda-environment/o/tenant1-pdb3/graph/fully-loaded-mlenv-manifest.json)
- graphenv-manifest.json (https://objectstorage.us-ashburn-1.oraclecloud.com/n/dwcsdev/b/conda-environment/o/tenant1-pdb3/graph/graphenv-manifest.json)