An AI profile is a specification that includes the AI provider to use and other details regarding metadata and database objects required for generating responses to natural language prompts.
An AI profile object can be created using select_ai.Profile()
Profile Object Model¶
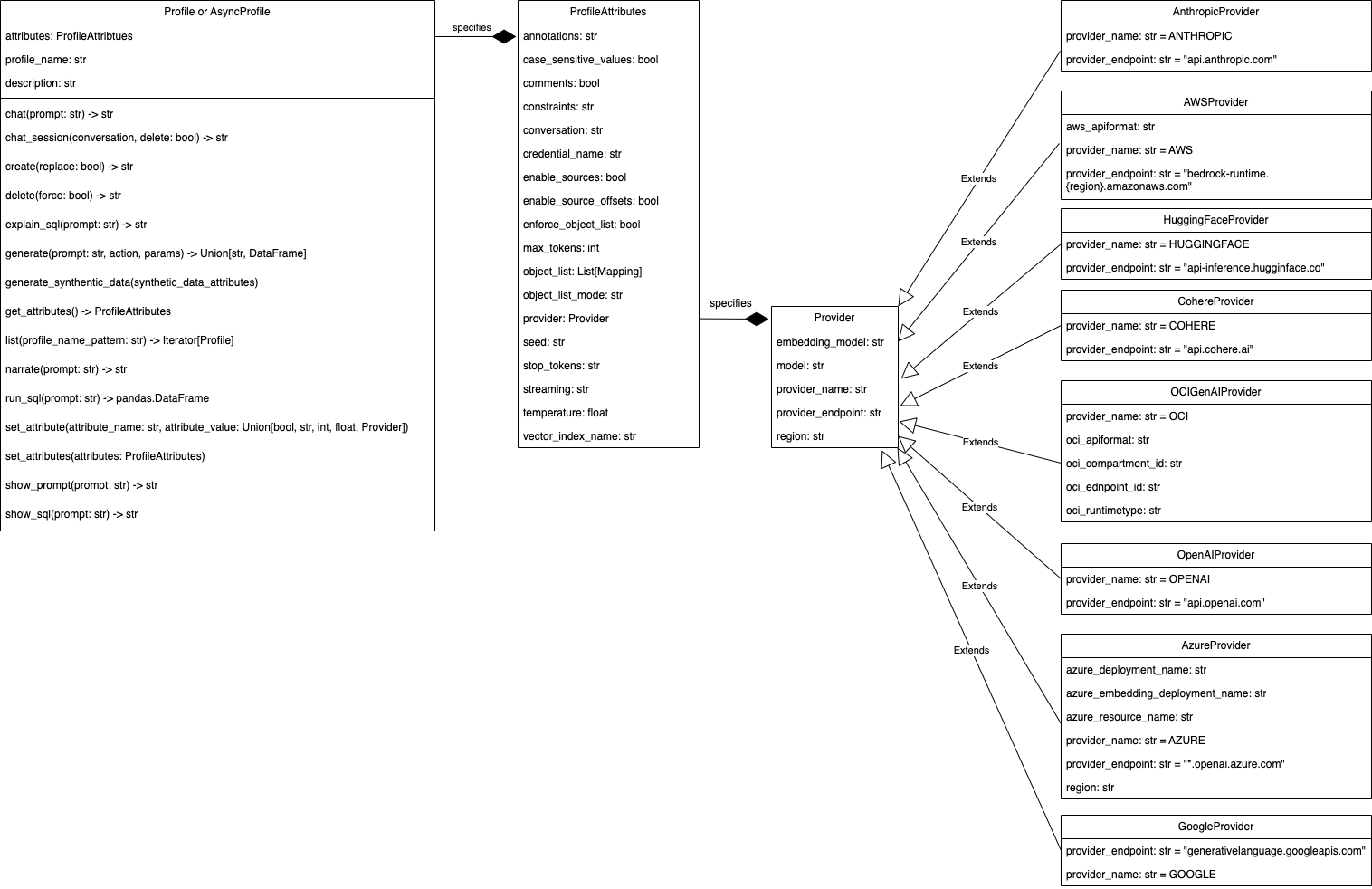
Base Profile API¶
- class select_ai.BaseProfile(profile_name: str | None = None, attributes: ProfileAttributes | None = None, description: str | None = None, merge: bool | None = False, replace: bool | None = False, raise_error_if_exists: bool | None = True, raise_error_on_empty_attributes: bool | None = False)¶
BaseProfile is an abstract base class representing a Profile for Select AI’s interactions with AI service providers (LLMs). Use either select_ai.Profile or select_ai.AsyncProfile to instantiate an AI profile object.
:param str profile_name : Name of the profile
- Parameters:
attributes (select_ai.ProfileAttributes) – Object specifying AI profile attributes
description (str) – Description of the profile
merge (bool) – Fetches the profile from database, merges the non-null attributes and saves it back in the database. Default value is False
replace (bool) – Replaces the profile and attributes in the database. Default value is False
raise_error_if_exists (bool) – Raise ProfileExistsError if profile exists in the database and replace = False and merge = False. Default value is True
raise_error_on_empty_attributes (bool) – Raise ProfileEmptyAttributesError, if profile attributes are empty in database. Default value is False.
Profile API¶
- class select_ai.Profile(*args, **kwargs)¶
Profile class represents an AI Profile. It defines attributes and methods to interact with the underlying AI Provider. All methods in this class are synchronous or blocking
- add_negative_feedback(prompt_spec: Tuple[str, Action] | None = None, sql_id: str | None = None, response: str | None = None, feedback_content: str | None = None)¶
Give negative feedback to the LLM
- Parameters:
prompt_spec (Tuple[str, Action]) – First element is the prompt and second is the corresponding action
sql_id (str) – SQL identifier from V$MAPPED_SQL view
response (str) – Expected SQL from LLM
feedback_content (str) – Actual feedback in natural language
- add_positive_feedback(prompt_spec: Tuple[str, Action] | None = None, sql_id: str | None = None)¶
Give positive feedback to the LLM
- Parameters:
prompt_spec (Tuple[str, Action]) – First element is the prompt and second is the corresponding action
sql_id (str) – SQL identifier from V$MAPPED_SQL view
- chat(prompt: str, params: Mapping = None) str¶
Chat with the LLM
- Parameters:
prompt (str) – Natural language prompt
params – Parameters to include in the LLM request
- Returns:
str
- chat_session(conversation: Conversation, delete: bool = False)¶
Starts a new chat session for context-aware conversations
- Parameters:
conversation (Conversation) – Conversation object to use for this chat session
delete (bool) – Delete conversation after session ends
- Returns:
- create(replace: int | None = False) None¶
Create an AI Profile in the Database
- Parameters:
replace (bool) – Set True to replace else False
- Returns:
None
- Raises:
oracledb.DatabaseError
- delete(force=False) None¶
Deletes an AI profile from the database
- Parameters:
force (bool) – Ignores errors if AI profile does not exist.
- Returns:
None
- Raises:
oracledb.DatabaseError
- delete_feedback(prompt_spec: Tuple[str, Action] = None, sql_id: str | None = None)¶
Delete feedback from the database
- Parameters:
prompt_spec (Tuple[str, Action]) – First element is the prompt and second is the corresponding action
sql_id (str) – SQL identifier from V$MAPPED_SQL view
- classmethod delete_profile(profile_name: str, force: bool = False)¶
Class method to delete an AI profile from the database
- Parameters:
profile_name (str) – Name of the AI profile
force (bool) – Ignores errors if AI profile does not exist.
- Returns:
None
- Raises:
oracledb.DatabaseError
- explain_sql(prompt: str, params: Mapping = None) str¶
Explain the generated SQL
- Parameters:
prompt (str) – Natural language prompt
params – Parameters to include in the LLM request
- Returns:
str
- classmethod fetch(profile_name: str) Profile¶
Create a proxy Profile object from fetched attributes saved in the database
- Parameters:
profile_name (str) – The name of the AI profile
- Returns:
select_ai.Profile
- Raises:
ProfileNotFoundError
- generate(prompt: str, action: Action | None = Action.RUNSQL, params: Mapping = None) DataFrame | str | None¶
Perform AI translation using this profile
- Parameters:
prompt (str) – Natural language prompt to translate
action (select_ai.profile.Action)
params – Parameters to include in the LLM request. For e.g. conversation_id for context-aware chats
- Returns:
Union[pandas.DataFrame, str]
- generate_synthetic_data(synthetic_data_attributes: SyntheticDataAttributes) None¶
Generate synthetic data for a single table, multiple tables or a full schema.
- Parameters:
synthetic_data_attributes (select_ai.SyntheticDataAttributes)
- Returns:
None
- Raises:
oracledb.DatabaseError
- get_attributes() ProfileAttributes¶
Get AI profile attributes from the Database
- Returns:
select_ai.ProfileAttributes
- classmethod list(profile_name_pattern: str = '.*') Generator[Profile, None, None]¶
List AI Profiles saved in the database.
- Parameters:
profile_name_pattern (str) – Regular expressions can be used to specify a pattern. Function REGEXP_LIKE is used to perform the match. Default value is “.*” i.e. match all AI profiles.
- Returns:
Iterator[Profile]
- narrate(prompt: str, params: Mapping = None) str¶
Narrate the result of the SQL
- Parameters:
prompt (str) – Natural language prompt
params – Parameters to include in the LLM request
- Returns:
str
- run_sql(prompt: str, params: Mapping = None) DataFrame¶
Run the generate SQL statement and return a pandas Dataframe built using the result set
- Parameters:
prompt (str) – Natural language prompt
params – Parameters to include in the LLM request
- Returns:
pandas.DataFrame
- set_attribute(attribute_name: str, attribute_value: bool | str | int | float | Provider)¶
Updates AI profile attribute on the Python object and also saves it in the database
- Parameters:
attribute_name (str) – Name of the AI profile attribute
attribute_value (Union[bool, str, int, float, Provider]) – Value of the profile attribute
- Returns:
None
- set_attributes(attributes: ProfileAttributes)¶
Updates AI profile attributes on the Python object and also saves it in the database
- Parameters:
attributes (ProviderAttributes) – Object specifying AI profile attributes
- Returns:
None
- show_prompt(prompt: str, params: Mapping = None) str¶
Show the prompt sent to LLM
- Parameters:
prompt (str) – Natural language prompt
params – Parameters to include in the LLM request
- Returns:
str
- show_sql(prompt: str, params: Mapping = None) str¶
Show the generated SQL
- Parameters:
prompt (str) – Natural language prompt
params – Parameters to include in the LLM request
- Returns:
str
- summarize(content: str = None, prompt: str = None, location_uri: str = None, credential_name: str = None, params: SummaryParams = None) str¶
Generate summary
- Parameters:
prompt (str) – Natural language prompt to guide the summary generation
content (str) – Specifies the text you want to summarize
location_uri (str) – Provides the URI where the text is stored or the path to a local file stored
credential_name (str) – Identifies the credential object used to authenticate with the object store
params (select_ai.summary.SummaryParams) – Parameters to include in the LLM request
- translate(text: str, source_language: str, target_language: str) str | None¶
Translate a text using a source language and a target language
- Parameters:
text (str) – Text to translate
source_language (str) – Source language
target_language (str) – Target language
- Returns:
str
Create Profile¶
import os
from pprint import pformat
import select_ai
user = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_USER")
password = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_PASSWORD")
dsn = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_DB_CONNECT_STRING")
select_ai.connect(user=user, password=password, dsn=dsn)
provider = select_ai.OCIGenAIProvider(
region="us-chicago-1", oci_apiformat="GENERIC"
)
profile_attributes = select_ai.ProfileAttributes(
credential_name="my_oci_ai_profile_key",
object_list=[{"owner": "SH"}],
provider=provider,
)
profile = select_ai.Profile(
profile_name="oci_ai_profile",
attributes=profile_attributes,
description="MY OCI AI Profile",
replace=True,
)
print("Created profile ", profile.profile_name)
profile_attributes = profile.get_attributes()
print(
"Profile attributes are: ",
pformat(profile_attributes.dict(exclude_null=False)),
)
output:
Created profile oci_ai_profile
Profile attributes are: {'annotations': None,
'case_sensitive_values': None,
'comments': None,
'constraints': None,
'conversation': None,
'credential_name': 'my_oci_ai_profile_key',
'enable_source_offsets': None,
'enable_sources': None,
'enforce_object_list': None,
'max_tokens': '1024',
'object_list': '[{"owner":"SH"}]',
'object_list_mode': None,
'provider': OCIGenAIProvider(embedding_model=None,
model=None,
provider_name='oci',
provider_endpoint=None,
region='us-chicago-1',
oci_apiformat='GENERIC',
oci_compartment_id=None,
oci_endpoint_id=None,
oci_runtimetype=None),
'seed': None,
'stop_tokens': None,
'streaming': None,
'temperature': None,
'vector_index_name': None}
Narrate¶
import os
import select_ai
user = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_USER")
password = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_PASSWORD")
dsn = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_DB_CONNECT_STRING")
select_ai.connect(user=user, password=password, dsn=dsn)
profile = select_ai.Profile(
profile_name="oci_ai_profile",
)
narration = profile.narrate(prompt="How many promotions?")
print(narration)
output:
There are 503 promotions in the database.
Show SQL¶
import os
import select_ai
user = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_USER")
password = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_PASSWORD")
dsn = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_DB_CONNECT_STRING")
select_ai.connect(user=user, password=password, dsn=dsn)
profile = select_ai.Profile(profile_name="oci_ai_profile")
sql = profile.show_sql(prompt="How many promotions ?")
print(sql)
output:
SELECT
COUNT("p"."PROMO_ID") AS "Number of Promotions"
FROM "SH"."PROMOTIONS" "p"
Run SQL¶
import os
import select_ai
user = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_USER")
password = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_PASSWORD")
dsn = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_DB_CONNECT_STRING")
select_ai.connect(user=user, password=password, dsn=dsn)
profile = select_ai.Profile(profile_name="oci_ai_profile")
df = profile.run_sql(prompt="How many promotions ?")
print(df.columns)
print(df)
output:
Index(['Number of Promotions'], dtype='object')
Number of Promotions
0 503
Chat¶
import os
import select_ai
user = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_USER")
password = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_PASSWORD")
dsn = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_DB_CONNECT_STRING")
select_ai.connect(user=user, password=password, dsn=dsn)
profile = select_ai.Profile(profile_name="oci_ai_profile")
response = profile.chat(prompt="What is OCI ?")
print(response)
output:
OCI stands for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. It is a comprehensive cloud computing platform provided by Oracle Corporation that offers a wide range of services for computing, storage, networking, database, and more.
...
...
OCI competes with other major cloud providers, including Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and IBM Cloud.
Summarize¶
Summarize inline content
import os
import select_ai
user = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_USER")
password = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_PASSWORD")
dsn = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_DB_CONNECT_STRING")
content = """
A gas cloud in our galaxy, Sagittarius B2, contains enough alcohol to brew 400
trillion pints of beer, and some stars are so cool that you could touch them
without being burned. Meanwhile, on the exoplanet 55 Cancri e, a form of
"hot ice" exists where high pressure prevents water from becoming gas even at
high temperatures. Additionally, some ancient stars found in the Milky Way's
halo are much older than the Sun, providing clues about the early universe and
its composition
"""
select_ai.connect(user=user, password=password, dsn=dsn)
profile = select_ai.Profile(profile_name="oci_ai_profile")
summary = profile.summarize(content=content)
print(summary)
output:
A gas cloud in the Sagittarius B2 galaxy contains a large amount of alcohol,
while some stars are cool enough to touch without being burned. The exoplanet
55 Cancri e has a unique form of "hot ice" where water remains solid despite
high temperatures due to high pressure. Ancient stars in the Milky Way's halo
are older than the Sun, providing insights into the early universe and its composition,
offering clues about the universe's formation and evolution.
Summarize content accessible via a URL
import os
import select_ai
user = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_USER")
password = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_PASSWORD")
dsn = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_DB_CONNECT_STRING")
select_ai.connect(user=user, password=password, dsn=dsn)
profile = select_ai.Profile(profile_name="oci_ai_profile")
summary = profile.summarize(
location_uri="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Astronomy"
)
print(summary)
output:
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena,
using mathematics, physics, and chemistry to explain their origin and evolution.
The field has a long history, with early civilizations making methodical
observations of the night sky, and has since split into observational and
theoretical branches. Observational astronomy focuses on acquiring data
from observations, while theoretical astronomy develops computer or
analytical models to describe astronomical objects and phenomena. The study
of astronomy has led to numerous discoveries, including the existence of
galaxies, the expansion of the universe, and the detection of gravitational
waves. Astronomers use various methods, such as radio, infrared, optical,
ultraviolet, X-ray, and gamma-ray astronomy, to study objects and events in
the universe. The field has also led to the development of new technologies and
has inspired new areas of research, such as astrobiology and the search for
extraterrestrial life. Overall, astronomy is a dynamic and constantly evolving
field that seeks to understand the universe and its many mysteries.
Translate¶
import os
import select_ai
user = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_USER")
password = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_PASSWORD")
dsn = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_DB_CONNECT_STRING")
select_ai.connect(user=user, password=password, dsn=dsn)
profile = select_ai.Profile(profile_name="oci_ai_profile")
response = profile.translate(
text="Thank you", source_language="en", target_language="de"
)
print(response)
output:
Danke
List profiles¶
import os
import select_ai
user = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_USER")
password = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_PASSWORD")
dsn = os.getenv("SELECT_AI_DB_CONNECT_STRING")
select_ai.connect(user=user, password=password, dsn=dsn)
profile = select_ai.Profile()
# matches all the profiles
for fetched_profile in profile.list():
print(fetched_profile.profile_name)
output:
ASYNC_OCI_AI_PROFILE
OCI_VECTOR_AI_PROFILE
ASYNC_OCI_VECTOR_AI_PROFILE
OCI_AI_PROFILE
Async Profile¶
- 1.
AsyncProfileAPIAsyncProfileAsyncProfile.add_negative_feedback()AsyncProfile.add_positive_feedback()AsyncProfile.chat()AsyncProfile.chat_session()AsyncProfile.create()AsyncProfile.delete()AsyncProfile.delete_feedback()AsyncProfile.delete_profile()AsyncProfile.explain_sql()AsyncProfile.fetch()AsyncProfile.generate()AsyncProfile.generate_synthetic_data()AsyncProfile.get_attributes()AsyncProfile.list()AsyncProfile.narrate()AsyncProfile.run_pipeline()AsyncProfile.run_sql()AsyncProfile.set_attribute()AsyncProfile.set_attributes()AsyncProfile.show_prompt()AsyncProfile.show_sql()AsyncProfile.summarize()AsyncProfile.translate()
- 2. Async Profile creation
- 3. Async explain SQL
- 4. Async run SQL
- 5. Async show SQL
- 6. Async concurrent SQL
- 7. Async chat
- 8. Summarize
- 9. Translate
- 10. Async pipeline
- 11. List profiles asynchronously