How to Use AG-UI with Agent Spec#
AG-UI is an open, event-based protocol and set of clients that connect agent backends to user interfaces for real-time, stateful, tool-aware experiences.
With the Agent Spec x AG-UI integration, you can take a portable Agent Spec configuration (JSON) and interact with it in AG-UI frontends, while keeping your choice of runtime (LangGraph, WayFlow). The adapter bridges Agent Spec Tracing and AG-UI events so frontends receive standardized messages, tool activity, and UI state without bespoke wiring.
In this guide, you will:
Configure an Agent Spec agent with a tool suitable for UI rendering
Expose AG-UI endpoints with FastAPI using the Agent Spec adapter
Run locally and connect an AG-UI client to any available runtime
See also
See the starter template project building AI agents using Agent Spec and CopilotKit.
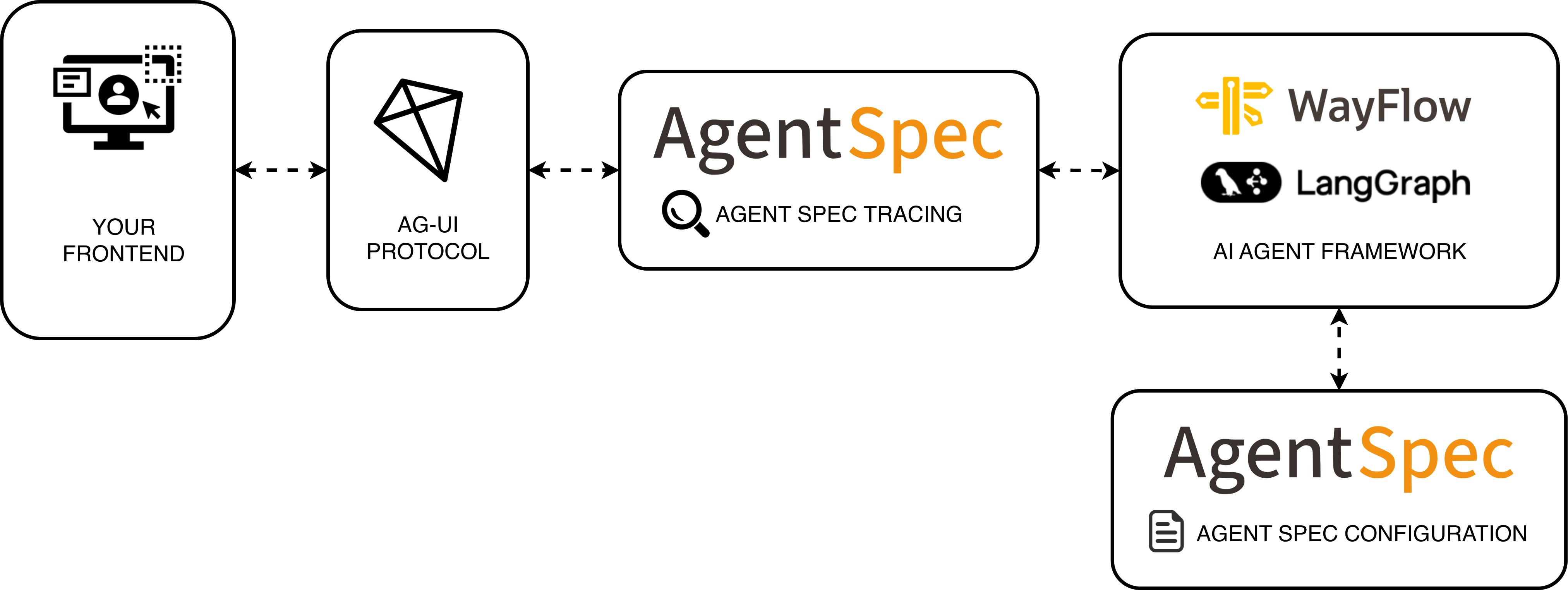
Prerequisites#
Python 3.10 to 3.13
Install the AG-UI Agent Spec integration from source:
git clone git@github.com:ag-ui-protocol/ag-ui.git
cd ag-ui/integrations/agent-spec/python
pip install -e .
This will install pyagentspec will the corresponding adapters for the different frameworks (LangGraph, WayFlow).
Step 1. Configure your Agent#
Create an agent with a tool that the UI can render and confirm. The example includes a weather tool and enables human-in-the-loop so the UI can request approvals before executing tools.
import os
from typing import Dict, Any
import dotenv
dotenv.load_dotenv()
from pyagentspec.agent import Agent
from pyagentspec.llms import OpenAiCompatibleConfig
from pyagentspec.tools import ServerTool
from pyagentspec.property import StringProperty
from pyagentspec.serialization import AgentSpecSerializer
def get_weather(location: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""
Get the weather for a given location.
"""
import time
time.sleep(1) # simulate tool execution
return {
"temperature": 20,
"conditions": "sunny",
"humidity": 50,
"wind_speed": 10,
"feelsLike": 25,
}
tool_input_property = StringProperty(
title="location",
description="The location to get the weather forecast. Must be a city/town name."
)
weather_result_property = StringProperty(title="weather_result")
weather_tool = ServerTool(
name="get_weather",
description="Get the weather for a given location.",
inputs=[tool_input_property],
outputs=[weather_result_property],
)
agent_llm = OpenAiCompatibleConfig(
name="my_llm",
model_id=os.environ.get("OPENAI_MODEL", "gpt-4o"),
url=os.environ.get("OPENAI_BASE_URL", "https://api.openai.com/v1")
)
agent = Agent(
name="my_agent",
llm_config=agent_llm,
system_prompt="Based on the weather forecaset result and the user input, write a response to the user",
tools=[weather_tool],
human_in_the_loop=True,
)
backend_tool_rendering_agent_json = AgentSpecSerializer().to_json(agent)
tool_registry = {"get_weather": get_weather}
This agent definition is exported to Agent Spec JSON and kept runtime-agnostic. The adapter will load it for any supported runtime.
Here is what the Agent Spec representation will look like ↓
Click here to see the assistant configuration.
{
"component_type": "Agent",
"id": "67ae0b68-53ab-458c-b8b7-43009ab81e34",
"name": "my_agent",
"description": null,
"metadata": {},
"inputs": [],
"outputs": [],
"llm_config": {
"component_type": "OpenAiCompatibleConfig",
"id": "c7dc111f-5c25-4aa0-8329-f6d44d578780",
"name": "my_llm",
"description": null,
"metadata": {},
"default_generation_parameters": null,
"url": "https://api.openai.com/v1",
"model_id": "gpt-4o"
},
"system_prompt": "Based on the weather forecaset result and the user input, write a response to the user",
"tools": [
{
"component_type": "ServerTool",
"id": "cd54932c-bda9-4021-aa12-110276bb86f3",
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Get the weather for a given location.",
"metadata": {},
"inputs": [
{
"description": "The location to get the weather forecast. Must be a city/town name.",
"title": "location",
"type": "string"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"title": "weather_result",
"type": "string"
}
]
}
],
"agentspec_version": "25.4.1"
}
component_type: Agent
id: 67ae0b68-53ab-458c-b8b7-43009ab81e34
name: my_agent
description: null
metadata: {}
inputs: []
outputs: []
llm_config:
component_type: OpenAiCompatibleConfig
id: c7dc111f-5c25-4aa0-8329-f6d44d578780
name: my_llm
description: null
metadata: {}
default_generation_parameters: null
url: https://api.openai.com/v1
model_id: gpt-4o
system_prompt: Based on the weather forecaset result and the user input, write a response
to the user
tools:
- component_type: ServerTool
id: cd54932c-bda9-4021-aa12-110276bb86f3
name: get_weather
description: Get the weather for a given location.
metadata: {}
inputs:
- description: The location to get the weather forecast. Must be a city/town name.
title: location
type: string
outputs:
- title: weather_result
type: string
agentspec_version: 25.4.1
Step 2: Configure a FastAPI endpoint#
Expose AG-UI endpoints with the Agent Spec adapter. The example auto-detects installed runtimes and mounts one endpoint per runtime:
/langgraph/backend_tool_renderingwhenlanggraphis installed/wayflow/backend_tool_renderingwhenwayflowcoreis installed
import os
import importlib.util
import logging
from fastapi import APIRouter, FastAPI
from ag_ui_agentspec.agent import AgentSpecAgent
from ag_ui_agentspec.endpoint import add_agentspec_fastapi_endpoint
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
router = APIRouter()
def _is_available(module_name: str) -> bool:
return importlib.util.find_spec(module_name) is not None
def _mount(router: APIRouter):
# LangGraph
if _is_available("langgraph"):
add_agentspec_fastapi_endpoint(
app=router,
agentspec_agent=AgentSpecAgent(
backend_tool_rendering_agent_json,
runtime="langgraph",
tool_registry=tool_registry,
),
path="/langgraph/backend_tool_rendering",
)
else:
logger.info("LangGraph not available. Skipping LangGraph endpoints.")
# Wayflow
# The comment mentioned 'wayflowcore' specifically
if _is_available("wayflowcore"):
add_agentspec_fastapi_endpoint(
app=router,
agentspec_agent=AgentSpecAgent(
backend_tool_rendering_agent_json,
runtime="wayflow",
tool_registry=tool_registry,
),
path="/wayflow/backend_tool_rendering",
)
else:
logger.info("Wayflow (wayflowcore) not available. Skipping Wayflow endpoints.")
# Create the Web App
app = FastAPI(title="Agent-Spec × AG-UI Examples")
_mount(router)
app.include_router(router)
port = int(os.getenv("PORT", "9003"))
# if __name__=="__main__":
# import uvicorn
# uvicorn.run("server:app", host="0.0.0.0", port=port, reload=True)
Run locally with Uvicorn (development only):
# If the app is in a module named "howto_ag_ui.py"
uvicorn howto_ag_ui:app --reload --port 8000
Important
This setup is intended for prototyping. Do not expose these endpoints publicly without proper authentication, rate limiting, and CORS controls.
Once the development server is running, navigate to your local AG-UI hosted website and you should see your Agent Spec + AG-UI + CopilotKit agents up and running.
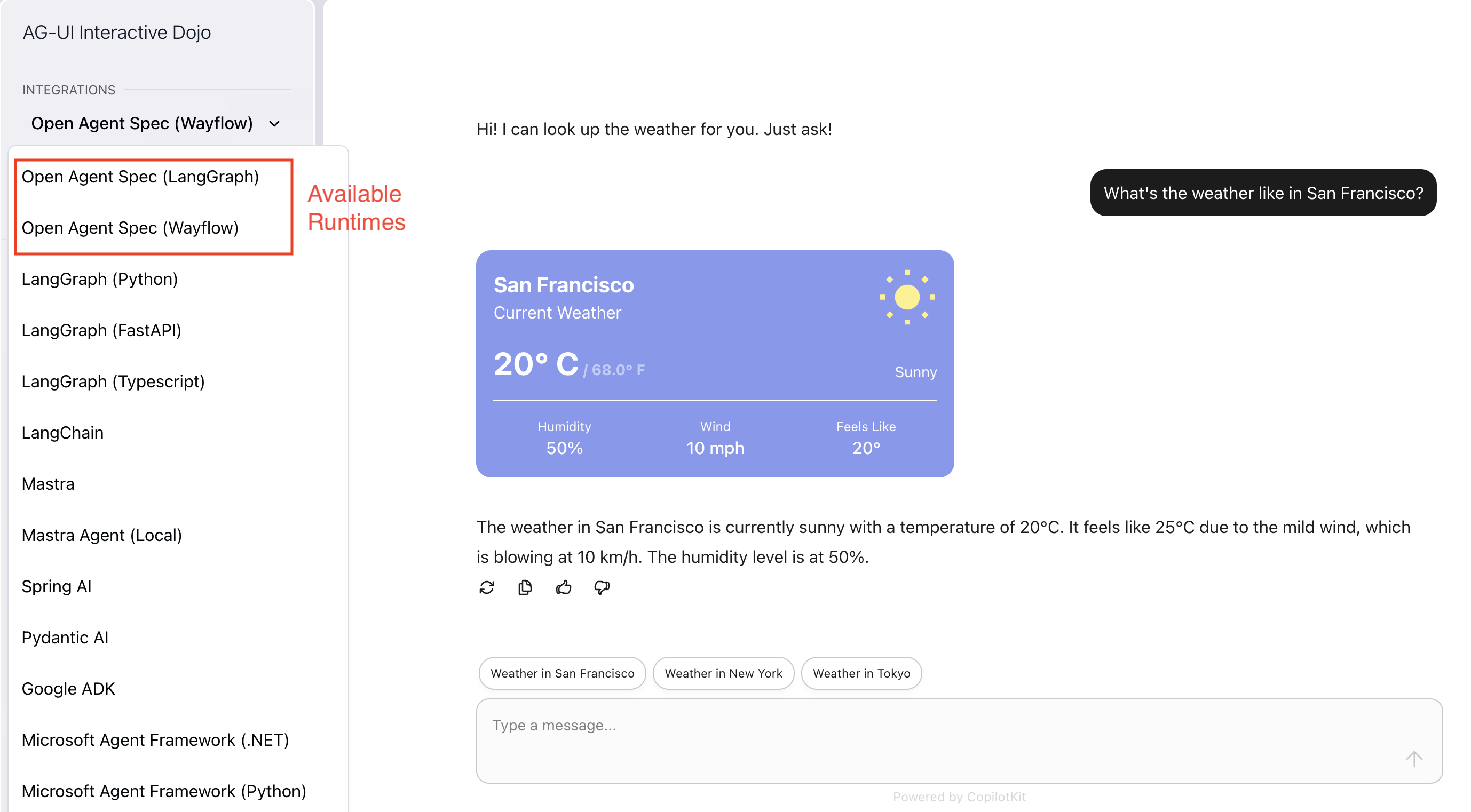
Note
The adapter maps Agent Spec Tracing spans/events to AG-UI events so frontends receive standardized messages and tool activity without extra glue code.
Recap#
In this guide you:
Defined an Agent Spec agent with a UI-renderable tool and HITL enabled
Exposed AG-UI endpoints via FastAPI for all available runtimes
Ran the server locally and prepared to connect an AG-UI client
Next steps#
Having learned how to connect Agent Spec agents to AG-UI, you may now proceed to: